Enhancing information security

Vulnerability Countermeasure Information Database JVN iPedia Registration Status [2020 4th Quarter (Oct. - Dec.)]
Release Date:Feb 17, 2021
IT Security Center
1. 2020 4th Quarter: Vulnerability Countermeasure Information Database JVN iPedia Registration Status
The vulnerability countermeasure information database JVN iPedia (https://jvndb.jvn.jp/en/) is endeavoring to become a comprehensive vulnerability database where vulnerability information is aggregated for easy access for IT users. JVN iPedia collects and/or translates the vulnerability information published by 1) domestic software developers, 2) JVN (*1), a vulnerability information portal run by JPCERT/CC and IPA, and 3) NVD (*2), a vulnerability database run by NIST (*3). JVN iPedia has been making vulnerability information available to the public since April 25, 2007.
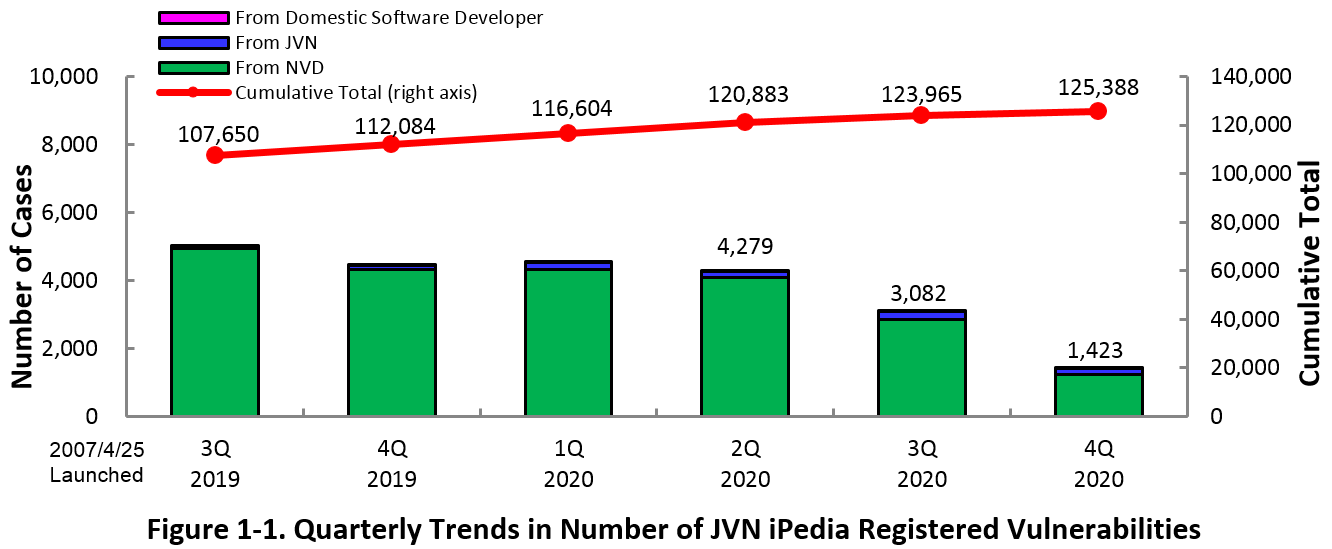
1-1. Vulnerabilities Registered in 2020/4Q
~ JVN iPedia now stores 125,388 vulnerabilities ~
The summary of the vulnerability information registered to the Japanese version of JVN iPedia during the 4th quarter of 2020 (October 1 to December 31, 2020) is shown in the table below. As of the end of December 2020, the total number of vulnerabilities stored in JVN iPedia is 125,388 (Table 1-1, Figure 1-1).
As for the JVN iPedia English version, the total number of vulnerabilities stored is 2,217 as shown in the lower half of the Table 1-1.
Table 1-1. Vulnerabilities Registered to JVN iPedia during 4th Quarter of 2020
|
|
Information Source
|
Registered Cases
|
Cumulative Cases
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Japanese Version
|
Domestic Product Developers
|
3 cases
|
246 cases
|
|
JVN
|
179 cases
|
9,705 cases
|
|
|
NVD
|
1,241 cases
|
115,437 cases
|
|
|
Total
|
1,423 cases
|
125,388 cases
|
|
|
English Version
|
Domestic Product Developers
|
3 cases
|
244 cases
|
|
JVN
|
26 cases
|
1,973 cases
|
|
|
Total
|
29 cases
|
2,217 cases
|
1-2. 【Observation 1】Vulnerability in Microsoft Server Products called “Zerologon”
~ Zerologon vulnerability(CVE-2020-1472)is classified as ‘Critical’, the highest severity. Many other vulnerabilities in Microsoft Server products are also classified as ‘Critical’. ~
Zerologon vulnerability (CVE-2020-1472) is a privilege escalation vulnerability discovered in the Netlogon Remote Protocol (MS-NRPC) used in the domain controller function of Windows Server products. If this vulnerability is exploited by attackers, it could lead to gaining domain admin privileges for a domain, theft of important confidential information of an organization, or taking over computers participating in the domain. When the vulnerability countermeasure information was provided by Microsoft in August 2020 (*4), the vulnerability was rated 10.0 in CVSSv3 rating scale. Since Microsoft later disclosed that it had confirmed an attack that exploits this vulnerability (*5), users had to address the vulnerability as soon as possible.
Microsoft released a patch for the Zerologon vulnerability (CVE-2020-1472) in August 2020. However, the Netlogon Remote Protocol is implemented in products other than Windows so Microsoft announced that the vulnerability will be addressed in two phases considering compatibility with those products (*6). Users of the software products and system administrators should refer to the dedicated guidance website provided by Microsoft, understand the work required at their organization and prepare to take immediate action when the second phase is released (scheduled to be released on February 9, 2021).
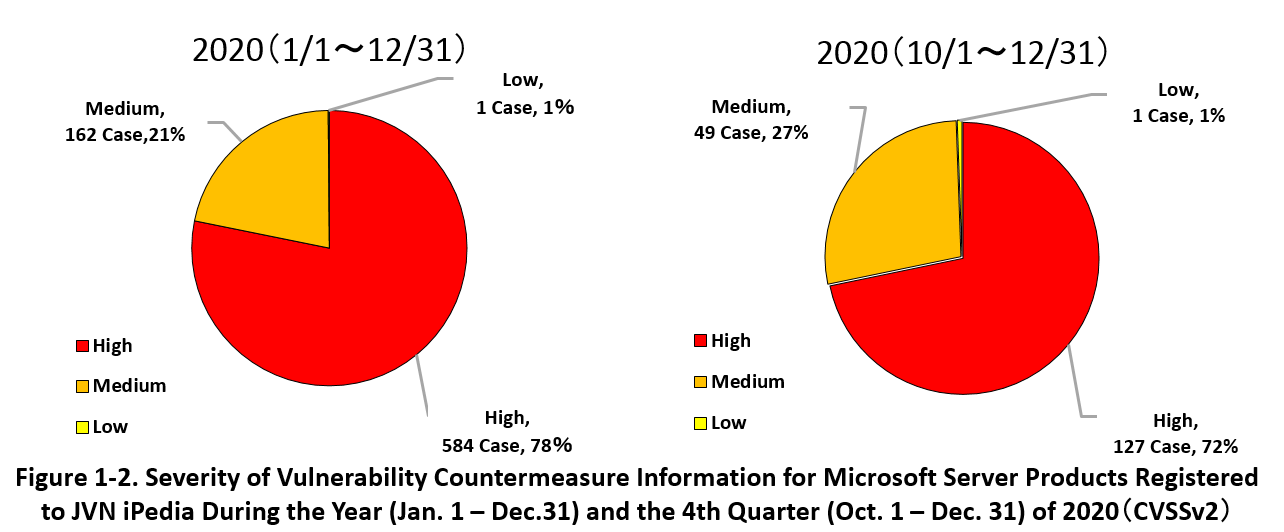
Other than the Zerologon vulnerability, many vulnerabilities in Microsoft Server products were disclosed in 2020.
Figure 1-2 shows the percentage of severity of vulnerability information for Microsoft Server products registered to JVN iPedia during the year (Jan. 1 – Dec.31) and the fourth quarter (Oct. 1 – Dec. 31) of 2020.
Of the vulnerabilities registered in the past year, 78% were classified as the highest severity "High" (Level III, CVSS Base Score=7.0–10.0) which can lead to serious damage, 21% as “Medium” (Level II, CVSS Base Score =4.0-6.9), and 1% as "Low" (Level II, CVSS Base Score = 0.1-3.9).
In the most recent fourth quarter (Oct. 1 to Dec. 31), the "High" vulnerability still accounted for 70% of the total, and the trend is likely to continue in 2021.
IPA publishes emergency countermeasure information for serious vulnerability attacks. For notifying the information quickly, IPA also provides the cyber security alert service "icat for JSON" (IPA Cyber security Alert Service for JavaScript Object Notation) (*7). Please take advantage of this service as well.
In addition, "icat" (Flash version) was discontinued on January 4, 2021 due to the discon-tinuation of Adobe Flash Player on December 31, 2020 (*8), so website administrators who have been using "icat" (Flash version) are requested to migrate to "icat for JSON" as soon as possible.
1-3. 【Observation 2】Vulnerability in Software Used in Telework, etc.
~ Cyber attacks targeting vulnerabilities in VPN products and web conferencing services have been occurred. Review security measures throughout the organization to ensure continuous telework. ~
Due to the impact of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, telework spread rapidly, but at the same time, cyber attacks targeting vulnerabilities in VPN products and web conferencing services used in telework environments have been carried out, and security agencies including IPA have called for caution regarding the conduct of telework.
Since many VPN products and web conferencing service software used in telework were used for the first time, or had not been used as it was installed for emergencies, users are supposed to continue to use the software without knowing where to collect information or how to apply updates in many cases.
However, if users continue to use the software without effective vulnerability countermeasures, there is a risk that attackers may exploit the vulnerability and leak software authentication information or confidential organizational information to the outside. In fact, it has been disclosed that attackers have been targeting telework environments to steal such important information (*9), so it is necessary to be very careful when conducting teleworking.
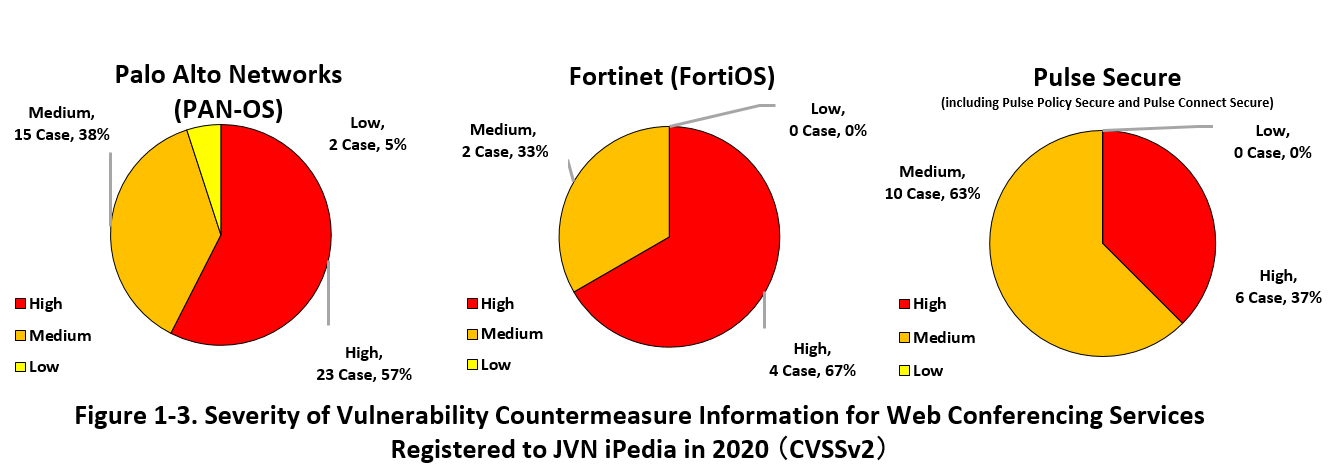
In 2019 and 2020, JPCERT/CC released alerts and other information about several VPN products that could be exploited (*10) (*11) (*12) (*13).
Figure 1-3 shows the percentage of severity of vulnerability countermeasure information registered to JVN iPedia in 2020 for the VPN products listed in the alerts. From left to right: Palo Alto Networks' VPN (PAN-OS), Fortinet's VPN (FortiOS), and Pulse Secure's VPN (including Pulse Policy Secure and Pulse Connect Secure).
The total number of vulnerabilities classified as "High" and "Medium" accounts for more than 95%, and it is required to take immediate action when vendors release fixes. Especially, vulnerabilities that have been alerted are highly likely to be exploited, so be sure to check updates for those vulnerabilities thoroughly.
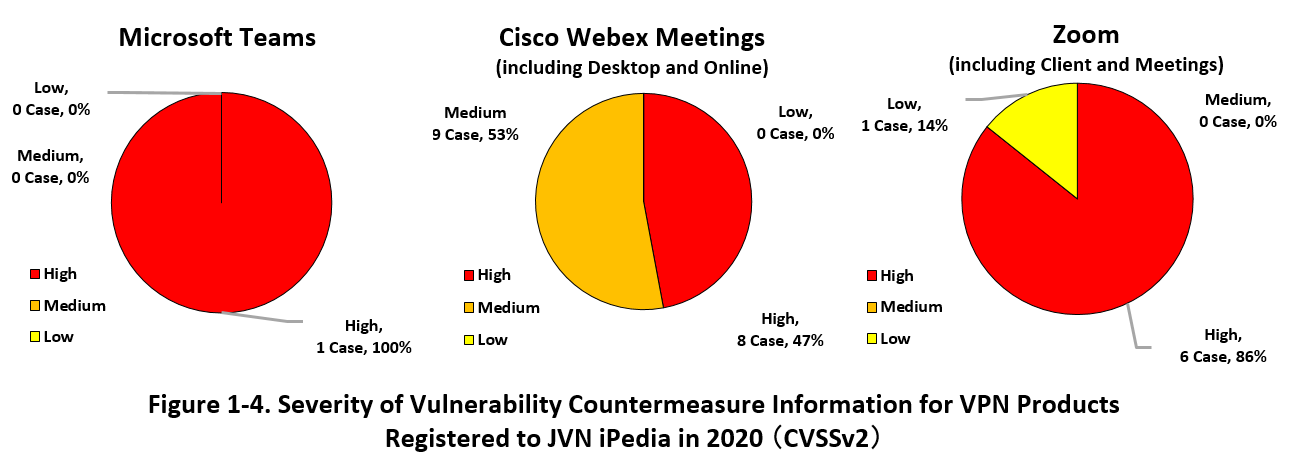
Figure 1-4 shows the percentage of severity of vulnerability countermeasure information registered to JVN iPedia in 2020 for the web conferencing services. From left to right: Microsoft Teams by Microsoft, Cisco Webex Meetings (including Desktop and Online) by Cisco System, Zoom Video From left to right: Microsoft Teams, Cisco Webex Meetings (including Desktop and Online), Zoom Video, and Zoom Communications (including Client and Meetings). Although the number of cases is small, it should be noted that the ratio of "High" and "Medium" is high as shown in Figure 1-3, so it is necessary to be very careful. IPA issued a warning regarding Zoom on April 3, 2020 (*14).
In order to prevent attacks that attempt to exploit vulnerabilities in VPN products and Web conferencing services, it is necessary to collect information on a regular basis regarding the vulnerability countermeasures of the software you are using, and to take countermeasures such as applying patches as soon as they are released by the vendor. When your organization has own servers, you need to take countermeasures not only for the software on the client side but also the software on the server side. In addition, it is important for system administrators to check for any evidence of cyberattacks from outside, etc., and review the organization's procedures and countermeasures as appropriate.
IPA publishes “Security Precautions for Teleworking” (*15) for workers in teleworking environments, and "Security Precautions for Using Web Conference Services" (*16) which summarizes key security points when using web conference services. Please refer to these documents before you start teleworking or web conference and prepare to ensure that it is conducted in a secure manner. In addition, when you continue to conduct telework, as the NISC (National Information Security Center) notifies (*17), it is also important to reevaluate information security risks and check and revise information security related regulations as necessary.
2. Details on JVN iPedia Registered Data
2-1. Types of Vulnerabilities Reported
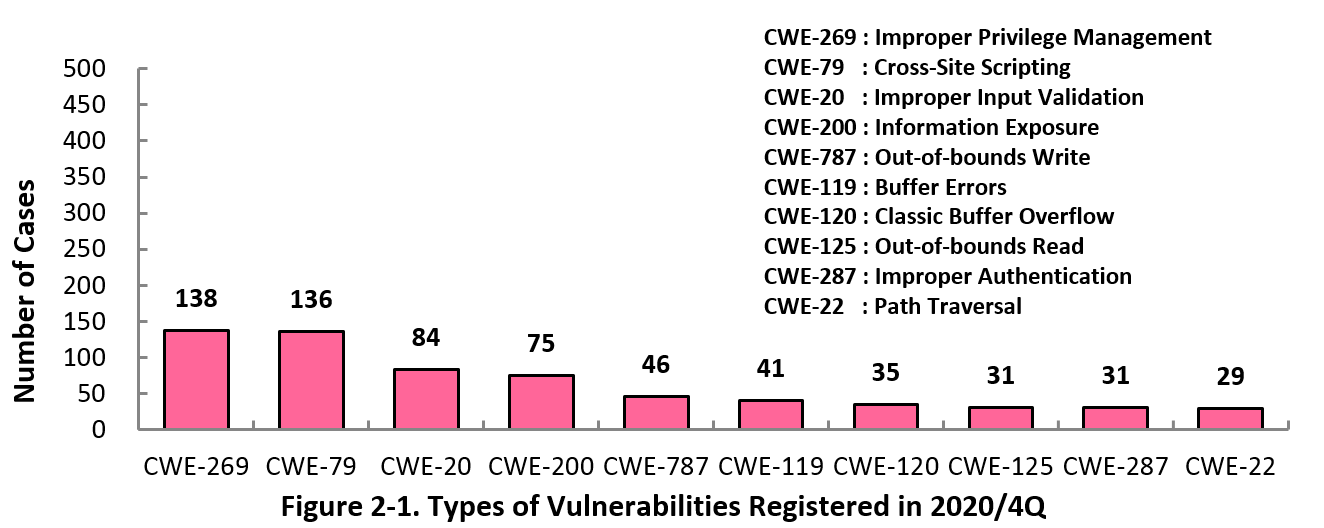
Figure 2-1 shows the number of vulnerabilities newly added to JVN iPedia during the 4th quarter of 2020, sorted by the CWE vulnerability types.
The type of the vulnerabilities reported most in the 4th quarter is CWE-269 (Improper Privilege Management) with 138 cases, followed by CWE-79 (Cross-Site Scripting) with 136 cases, CWE-20 (Improper Input Validation) with 84, CWE-200 (Information Exposure) with 75, CWE-787 (Out-of-bounds Write) with 46.
CWE-269 (Improper Privilege Management), the most reported vulnerability type in this quarter, can be exploited to gain administrator privileges and manipulate the system.
Software developers need to make sure to mitigate vulnerability from the planning and design phase of software development. IPA provides tools and guidelines, such as "Vulnerability Countermeasure Guide for Software Developers"" (*18), "How to Secure Your Website" (*19), "Secure Programming Guide" (*20) and "AppGoat" (*21), a hands-on venerability learning tool, for website developers and operators to build secure websites.
2-2. Severity of Vulnerabilities Reported
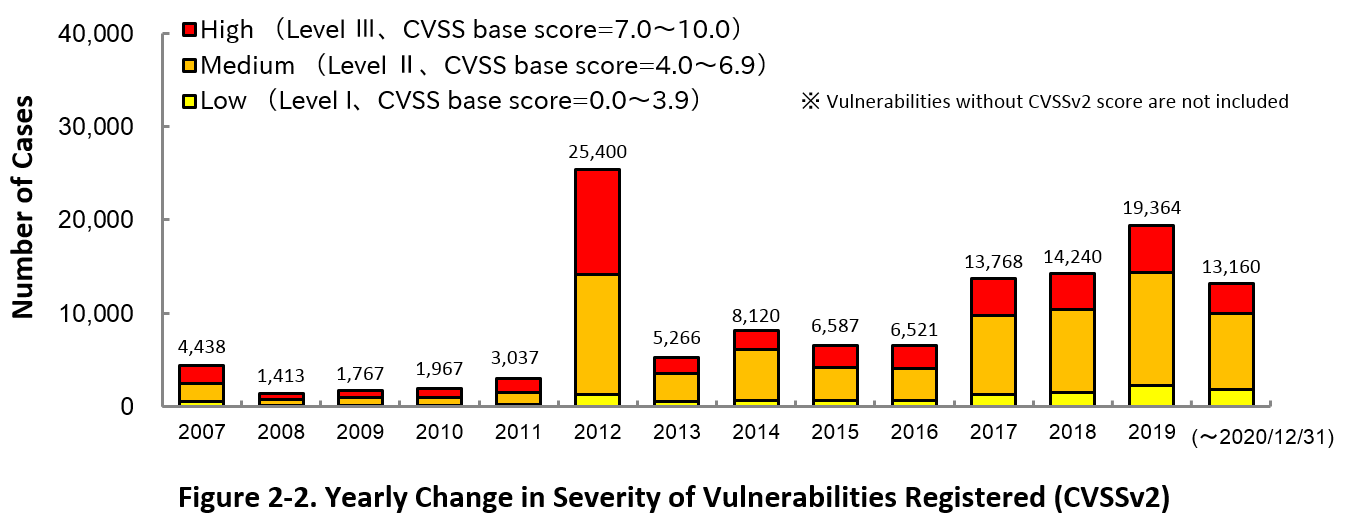
Figure 2-2 shows the yearly change in the CVSSv2 rating scale based severity of vulnerabilities registered to JVN iPedia.
As for the vulnerabilities added to JVN iPedia in 2020, 23.7 percent are “Level III” (7.0 - 10.0), 61.9 percent are “Level ll” (4.0 – 6.9) and 14.4 percent are “Level I” (0.0 – 3.9). This means 85.6 percent of all vulnerabilities registered are Level II or higher, which are potentially critical enough to cause damage like information exposure or data falsification.
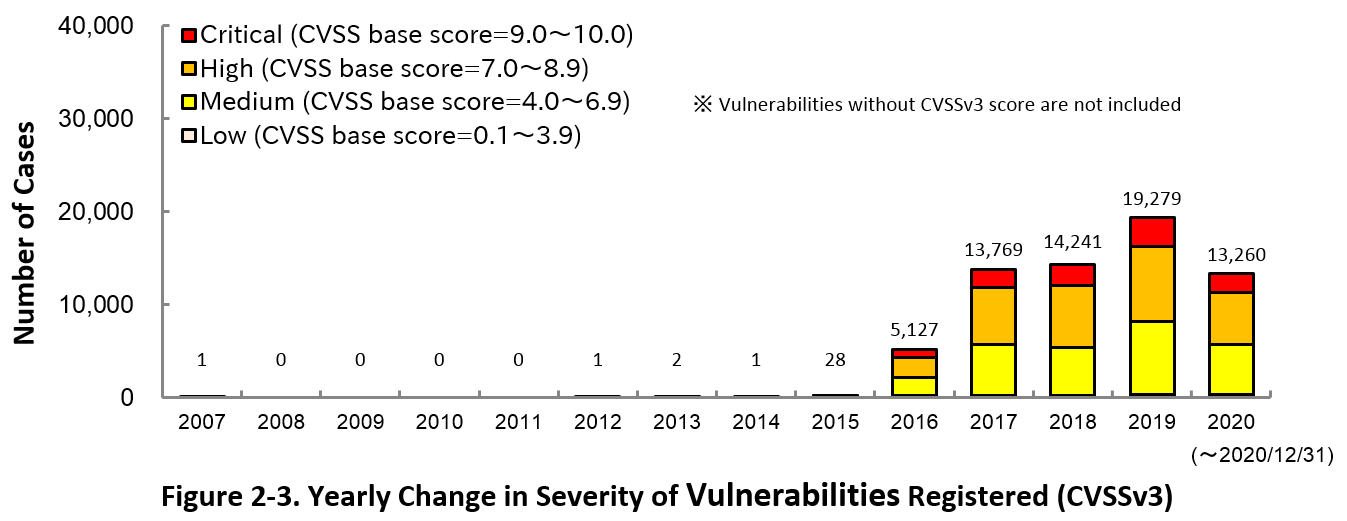
Figure 2-3 shows the yearly change in the CVSSv3 rating scale based severity of vulnerabilities registered to JVN iPedia.
As for the vulnerabilities added to JVN iPedia in 2020, 14.8 percent are “Critical” (9.0 – 10.0), 42.5 percent are “High” (7.0 – 8.9), 40.6 percent are “Medium” (4.0 – 6.9) and 2.1 percent are “Low” (0.1 – 3.9).
To avoid threats posed by the known vulnerabilities, both product developers and IT users should pay close attention to vulnerability disclosure and update software they use to a fixed version or apply a security patch as soon as possible when they become available. IT users can check vulnerabilities newly published on JVN iPedia in RSS and XML format (*22) as well.
2-3. Types of Software Reported with Vulnerability
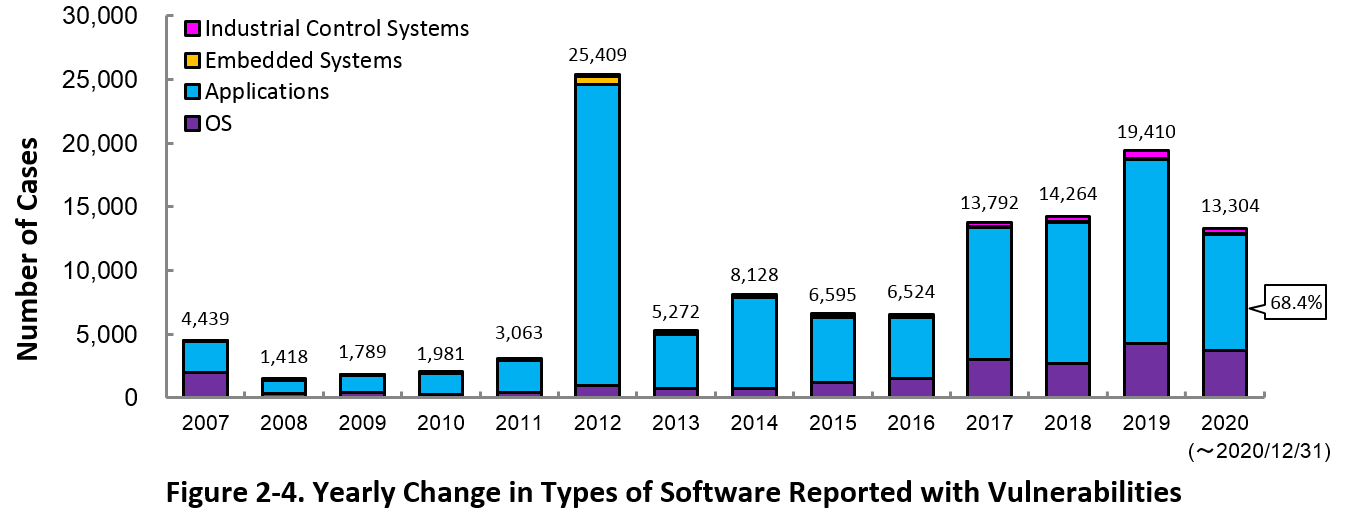
Figure 2-4 shows the yearly change in the type of software reported with vulnerability. Application vulnerabilities have been published most, accounting for 68.4 percent (9,104 out of 13,304) of the 2020 total.
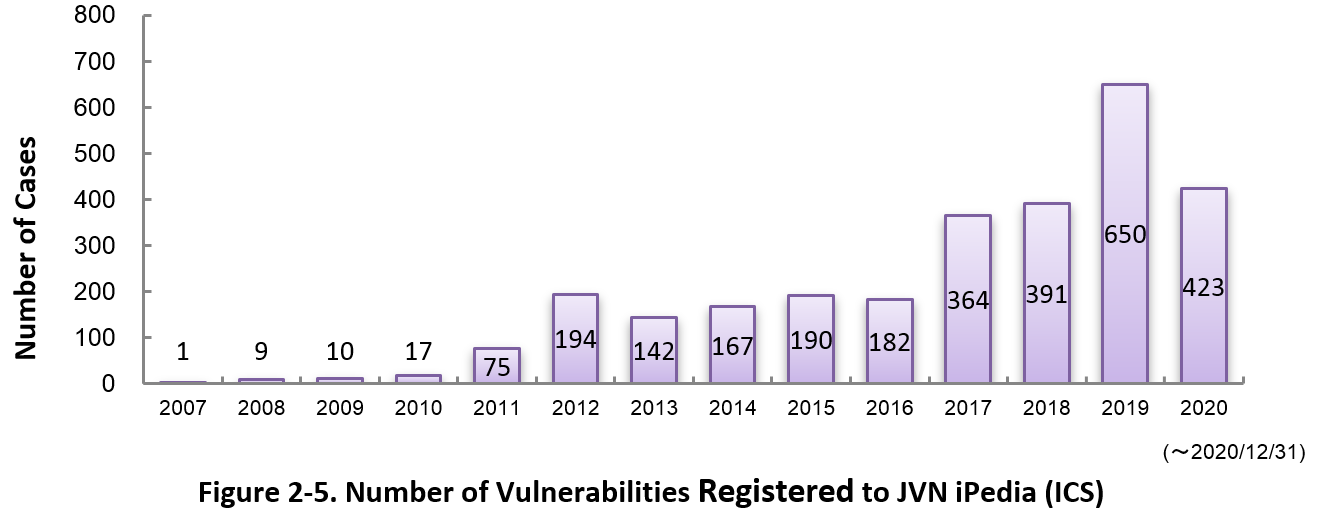
Figure 2-5 shows the yearly change in the number of JVN iPedia-stored vulnerabilities in industrial control systems (ICS) used in critical infrastructure sectors. As of December 2020, the total of 2,815 ICS vulnerabilities have been registered.
2-4. Products Reported with Vulnerability
Table 2-1 lists the top 20 software whose vulnerabilities were most registered to JVN iPedia during the 4th quarter (October to December) of 2020.
In this quarter, the 1st rank continued to be Microsoft Windows 10 from the previous quarter. From 2nd to 20th, other Windows OS products are also ranked.
Besides those in the top 20 list, JVN iPedia stores and offers vulnerability information about a variety of software. IPA hopes software developers and users will make good use of JVN iPedia to efficiently check vulnerability information and take necessary action in a timely manner (*23).
Table 2-1. Top 20 most registered software products vulnerability countermeasure information in JVN iPedia [Oct. – Dec. 2020]
|
Rank
|
Category
|
Product Name (Vendor)
|
Number of
Vulnerabilities Registered |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1
|
OS
|
Microsoft Windows 10 (Microsoft)
|
184
|
|
2
|
OS
|
Microsoft Windows Server (Microsoft)
|
177
|
|
3
|
OS
|
Microsoft Windows Server 2019 (Microsoft)
|
165
|
|
4
|
OS
|
Microsoft Windows Server 2016 (Microsoft)
|
143
|
|
5
|
OS
|
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 (Microsoft)
|
96
|
|
6
|
OS
|
Microsoft Windows 8.1 (Microsoft)
|
86
|
|
6
|
OS
|
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 (Microsoft)
|
86
|
|
8
|
OS
|
Microsoft Windows RT 8.1 (Microsoft)
|
83
|
|
9
|
OS
|
Microsoft Windows 7 (Microsoft)
|
78
|
|
10
|
Firmware
|
Qualcomm component (Qualcomm)
|
69
|
|
11
|
Middleware
|
MySQL (Oracle)
|
48
|
|
12
|
OS
|
iOS (Apple)
|
46
|
|
12
|
OS
|
iPadOS (Apple)
|
46
|
|
14
|
Web-based collaborative platform
|
Microsoft SharePoint Server (Microsoft)
|
36
|
|
15
|
OS
|
Apple Mac OS X (Apple)
|
35
|
|
16
|
OS
|
watchOS (Apple)
|
34
|
|
17
|
Web-based collaborative platform
|
Microsoft SharePoint Enterprise Server (Microsoft)
|
33
|
|
18
|
OS
|
tvOS (Apple)
|
32
|
|
19
|
Business Software
|
Microsoft Office (Microsoft)
|
29
|
|
19
|
Business Software
|
Microsoft 365 Apps (Microsoft)
|
29
|
3. Most Accessed Vulnerability Countermeasure Information
Table 3-1 lists the top 20 most accessed vulnerability countermeasure information in JVN iPedia during the 4th quarter of 2020 (October to December).
In this quarter, 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 9th ranks are vulnerability countermeasure information related to WordPress. This was due to a large number of accesses that appeared to be mechanical from a certain organization.
Rating Scale
Note 1) CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
- Level I (Low)
- CVSS Base Score = 0.0~3.9
- Level II (Medium)
- CVSS Base Score = 4.0~6.9
- Level III (High)
- CVSS Base Score = 7.0~10.0
Note 2) CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
- Low
- CVSS Base Score =0.1~3.9
- Medium
- CVSS Base Score =4.0~6.9
- High
- CVSS Base Score =7.0~8.9
- Critical
- CVSS Base Score =9.0~10.0
Table 3-1. Top 20 Most Accessed Vulnerability Countermeasure Information in JVN iPedia [Oct. – Dec. 2020]
No.1 Cross-site Scripting Vulnerability in WordPress JVNDB-2020-006830
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
- Level I (Low)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
3.5
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
- Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
5.4
- Date Public
-
2020/7/20
- Access Count
-
10,787
No.2 Cross-site Scripting Vulnerability in WordPress JVNDB-2020-006831
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
- Level I (Low)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
3.5
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
6.8
- Date Public
-
2020/7/20
- Access Count
-
10,646
No.3 WordPress Vulnerable to Authentication Bypass Using an Alternate Path or Channel JVNDB-2020-006893
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
6.0
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Low
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
3.1
- Date Public
-
2020/7/22
- Access Count
-
10,636
No.4 Cross-site Scripting Vulnerability in WordPress JVNDB-2020-006788
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level I (Low)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
3.5
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Low
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
2.4
- Date Public
-
2020/7/17
- Access Count
-
10,620
No5. Out-of-bounds Write Vulnerability in Firefox and Thunderbird JVNDB-2020-009481
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level III (High)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
9.3
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
8.8
- Date Public
-
2020/11/9
- Access Count
-
9,504
No.6 Hibernate ORM vulnerable to SQL injection JVNDB-2020-000074
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
- Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
4.0
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
- High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
7.4
- Date Public
-
2020/11/19
- Access Count
-
9,393
No.7 Path Traversal Vulnerability in KDE Ark JVNDB-2020-009073
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
- Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
4.3
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Low
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
3.3
- Date Public
-
2020/10/16
- Access Count
-
9,226
No.8 OS command injection vulnerability in multiple ELECOM LAN routers JVNDB-2020-000067
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
5.8
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
8.8
- Date Public
-
2020/10/5
- Access Count
-
9,136
No.9 Open Redirect Vulnerability in WordPress JVNDB-2020-006832
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
4.9
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
5.7
- Date Public
-
2020/7/20
- Access Count
-
8,938
No.10 InfoCage SiteShell installs their files with improper access permissions JVNDB-2020-000066
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
6.8
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
7.8
- Date Public
-
2020/9/30
- Access Count
-
8,852
No.11 Kubernetes ingress-nginx component vulnerable to Externally Controlled Reference to a Resource in Another Sphere JVNDB-2020-008942
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
- Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
4.9
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
- Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
5.9
- Date Public
-
2020/10/8
- Access Count
-
8,849
No.12 Incorrect Default Permissions Vulnerability in Cloudera CDH JVNDB-2018-016161
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
- Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
6.5
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
7.2
- Date Public
-
2019/12/16
- Access Count
-
8,594
No.13 Trend Micro Antivirus for Mac vulnerable to a privilege escalation JVNDB-2020-008931
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
-
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
7.8
- Date Public
-
2020/10/7
- Access Count
-
8,321
No.14 CMONOS.JP vulnerable to cross-site scripting JVNDB-2020-008821
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
-
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
6.1
- Date Public
-
2020/9/28
- Access Count
-
8,010
No.15 JavaFX WebEngine does not properly restrict Java method execution JVNDB-2020-000047
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
6.8
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
8.8
- Date Public
-
2020/7/28
- Access Count
-
7,933
No.16 Multiple vulnerabilities in XOOPS module "XooNIps" JVNDB-2020-009467
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
-
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
- Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
6.3
- Date Public
-
2020/11/9
- Access Count
-
7,796
No.17 Multiple vulnerabilities in TCP/IP function on Mitsubishi Electric GOT2000 series JVNDB-2020-006469
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
-
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Critical
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
9.8
- Date Public
-
2020/7/9
- Access Count
-
7,695
No.18 WordPress Plugin "Live Chat - Live support" vulnerable to cross-site request forgery JVNDB-2020-000068
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level I (Low)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
2.6
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
4.3
- Date Public
-
2020/10/14
- Access Count
-
7,663
No.19 Cross-site Scripting Vulnerability in phpMyAdmin JVNDB-2014-003893
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level I (Low)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
3.5
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
-
- Date Public
-
2014/8/25
- Access Count
-
7,661
No.20 Apache Struts 2 vulnerable to denial-of-service (DoS) JVNDB-2020-000055
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
4.3
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
5.9
- Date Public
-
2020/8/25
- Access Count
-
7,629
Table 3-2 lists the top 5 most accessed vulnerability information among those reported by domestic product developers.
Table 3-2. Top 5 Most Accessed Vulnerabilities Reported by Domestic Product Developers [Oct. - Dec. 2020]
No.1 DoS Vulnerability in HiRDB JVNDB-2020-007128
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
- -
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
- -
- Date Public
-
2020/8/3
- Access Count
-
4,474
No.2 Multiple Vulnerabilities in Hitachi Command Suite, Hitachi Automation Director, Hitachi Configuration Manager, Hitachi Infrastructure Analytics Advisor and Hitachi Ops Center JVNDB-2020-007127
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
- -
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
-
- Date Public
-
2020/8/3
- Access Count
-
4,467
No.3 Cross-site Scripting Vulnerability in Hitachi Infrastructure Analytics Advisor and Hitachi Ops Center Analyzer JVNDB-2020-006617
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
-
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
-
- Date Public
-
2020/7/14
- Access Count
-
4,327
No.4 Vulnerability in Cosminexus HTTP Server JVNDB-2020-005743
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
-
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
-
- Date Public
-
2020/6/22
- Access Count
-
4,270
No.5 Vulnerability in Cosminexus HTTP Server and Hitachi Web Server JVNDB-2019-010374
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
-
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
-
- Date Public
-
2019/10/11
- Access Count
-
4,266
Footnotes
-
(*1)
-
(*2)
-
(*3)
-
(*4)
-
(*5)
-
(*6)
-
(*7)
-
(*8)
-
(*9)
-
(*10)
-
(*11)
-
(*12)
-
(*13)
-
(*14)
-
(*15)
-
(*16)
-
(*17)
-
(*18)
-
(*19)
-
(*20)
-
(*21)
-
(*22)
-
(*23)
Past Quarterly Reports
Contact information
IT Security Center, Information-technology Promotion Agency, Japan (ISEC/IPA)