Enhancing information security

Vulnerability Countermeasure Information Database JVN iPedia Registration Status [2025 2nd Quarter (Apr. - Jun.)]
Release Date:Aug 20, 2025
IT Security Center
1. 2025 2nd Quarter: Vulnerability Countermeasure Information Database JVN iPedia Registration Status
The vulnerability countermeasure information database JVN iPedia is endeavoring to become a comprehensive vulnerability database where vulnerability information is aggregated for easy access for IT users. JVN iPedia collects and/or translates the vulnerability information published by 1) domestic software developers, 2) JVN (footnote 1), a vulnerability information portal run by JPCERT/CC and IPA, and 3) NVD (footnote 2), a vulnerability database run by NIST (footnote 3). JVN iPedia has been making vulnerability information available to the public since April 25, 2007.
1-1. Vulnerabilities Registered in the 2nd Quarter of 2025
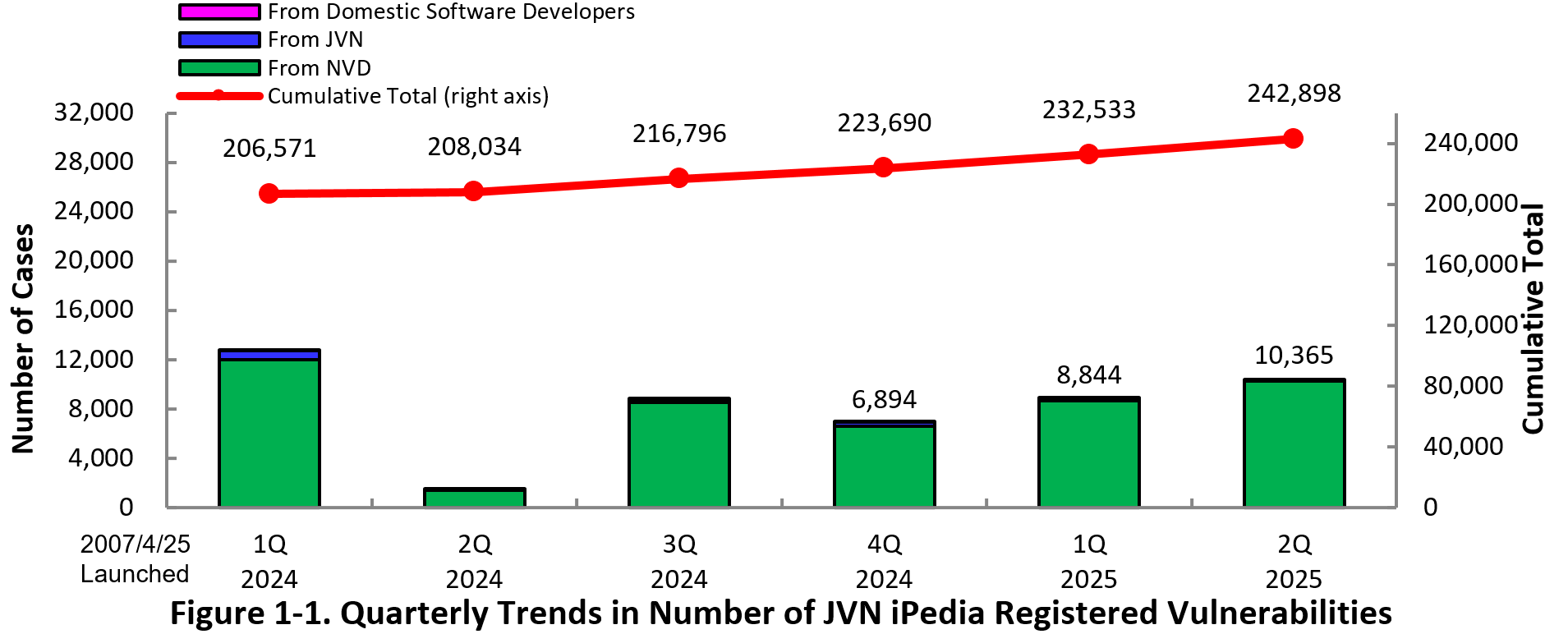
JVN iPedia now stores 242,898 vulnerabilities
The summary of the vulnerability information registered to the Japanese version of JVN iPedia during the second quarter (April 1 to June 30) of 2025 is shown in the table below. As of the end of June 2025, the total number of vulnerabilities stored in JVN iPedia is 242,898 (Table 1-1, Figure 1-1).
The reason for the increase in registrations on JVN iPedia in the second quarter of 2025 is due to an increase in vulnerability disclosures on NVD during this period.
As for the JVN iPedia English version, the total number of vulnerabilities stored is 3,016 as shown in the Table 1-2.
Table 1-1. Vulnerabilities Registered in JVN iPedia in the 2nd Quarter of 2025 (Japanese Version)
| Information Source | Registered Cases | Cumulative Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Domestic Software Developers | 0 cases | 291 cases |
| JVN | 136 cases | 16,447 cases |
| NVD | 10,229 cases | 226,160 cases |
| Total | 10,365 cases | 242,898 cases |
Table 1-2. Vulnerabilities Registered in JVN iPedia in the 2nd Quarter of 2025 (English Version)
| Information Source | Registered Cases | Cumulative Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Domestic Software Developers | 0 cases | 294 cases |
| JVN | 39 cases | 2,722 cases |
| Total | 39 cases | 3,016 cases |
2. Details on JVN iPedia Registered Data
2-1. Types of Vulnerabilities Reported
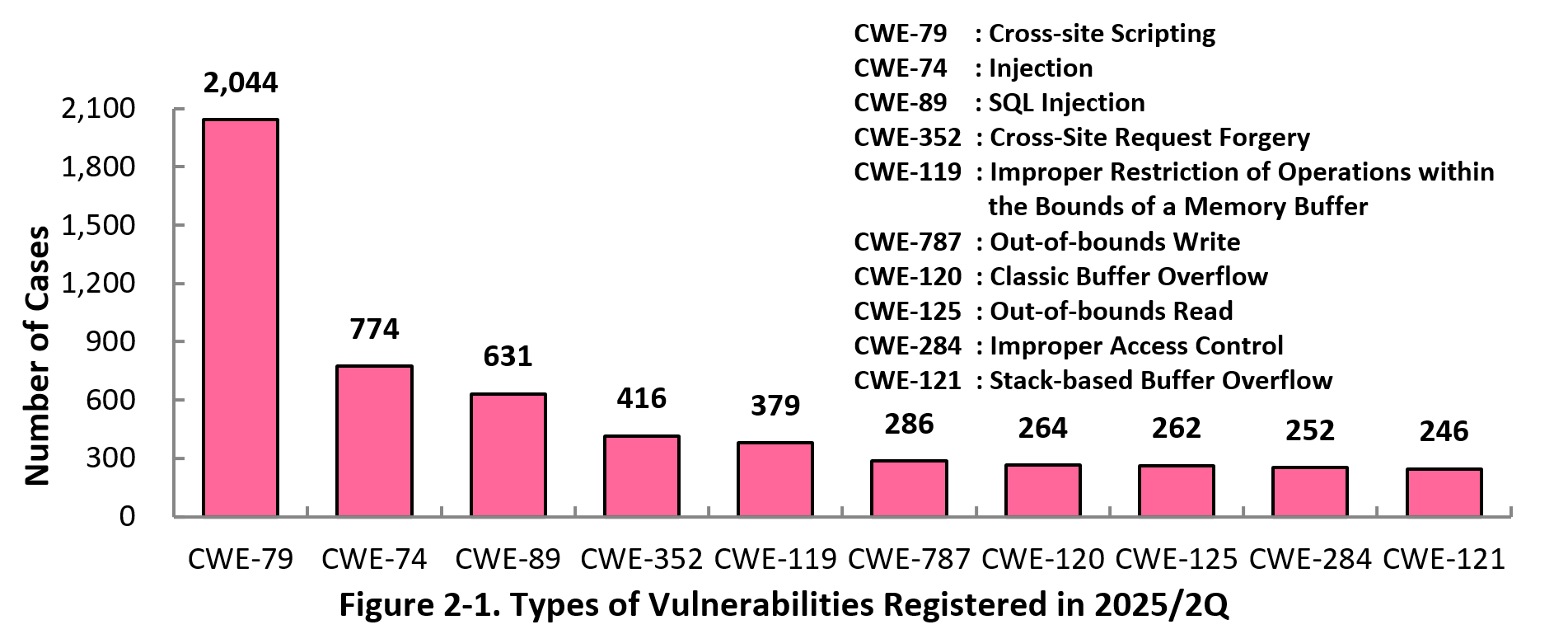
Figure 2-1 shows the number of vulnerabilities newly added to JVN iPedia during the second quarter (April 1 to June 30) of 2025, sorted by the CWE vulnerability types.
The type of the vulnerabilities reported most in the second quarter is CWE-79 (Cross-Site Scripting) with 2,044 cases, followed by CWE-74 (Injection) with 774, CWE-89 (SQL Injection) with 631, CWE-352 (Cross-Site Request Forgery) with 416, CWE-119 (Improper Restriction of Operations within the Bounds of a Memory Buffer) with 379. CWE-79 (Cross-site Scripting), the most reported vulnerability type in this quarter, could allow attackers to display false webpages and/or steal information.
Software developers need to make sure to mitigate vulnerability from the planning and design phase of software development. IPA provides tools and guidelines, such as “Vulnerability Countermeasure Guide for Software Developers” (footnote 4), “How to Secure Your Web-site” (footnote 5), and “AppGoat” (footnote 6), a hands-on venerability learning tool, for website developers and operators to build secure websites.
2-2. Severity of Vulnerabilities Reported
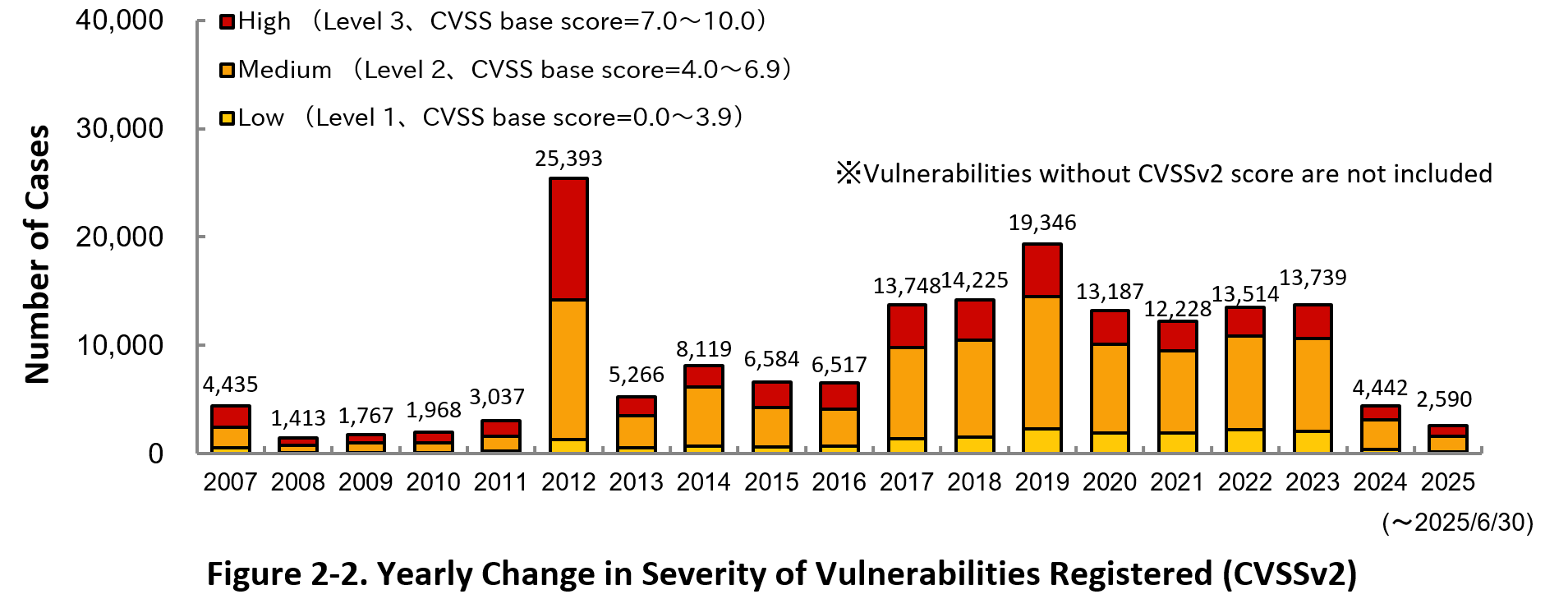
Figure 2-2 shows the yearly change in the CVSSv2 rating scale based severity of vulnerabilities registered to JVN iPedia.
As for the vulnerabilities added to JVN iPedia in 2025, 38.2 percent are “Level 3” (7.0 - 10.0), 54.3 percent are “Level 2” (4.0 – 6.9) and 7.5 percent are “Level 1” (0.0 – 3.9). This means 92.5 percent of all vulnerabilities registered are Level 2 or higher, which are potentially critical enough to cause damage like information exposure or data falsification.
The reason for the significant decrease in the number of CVSSv2 registrations in JVN iPedia in 2024 is that CVSSv2 is not actively evaluated by NVD, the information collection source for JVN iPedia (footnote 7).
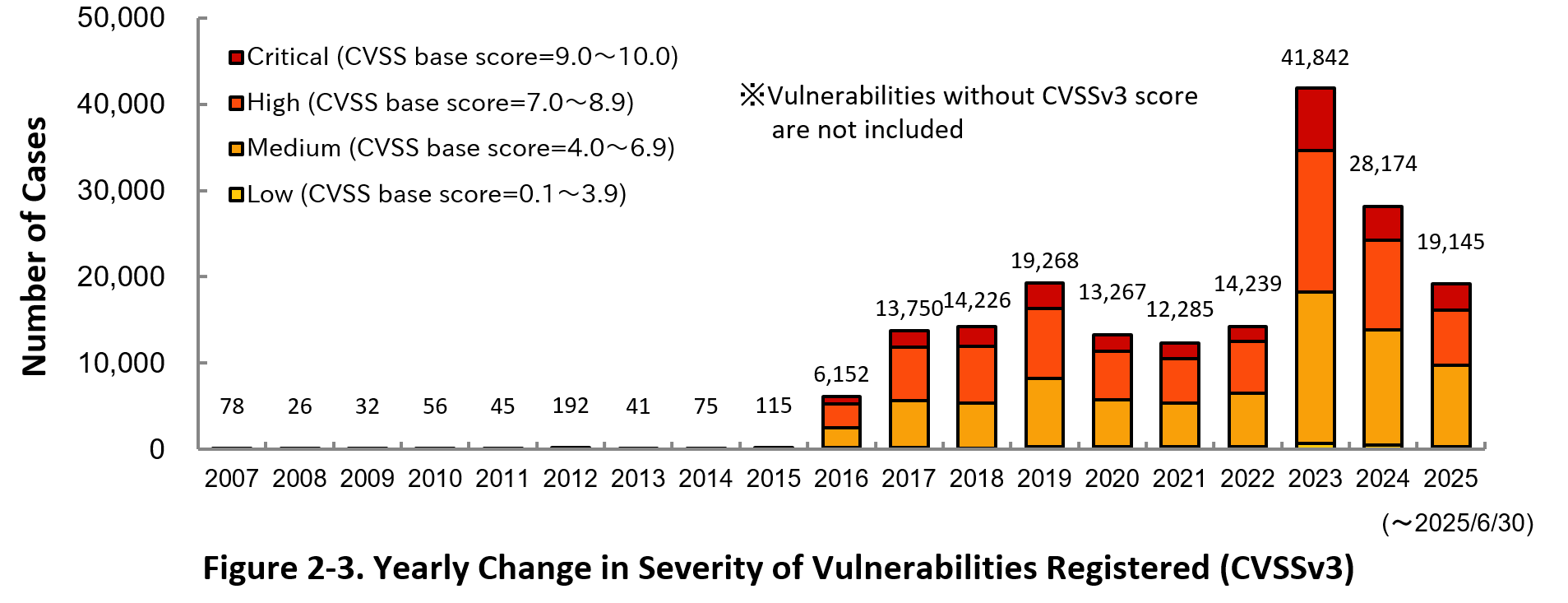
Figure 2-3 shows the yearly change in the CVSSv3 rating scale based severity of vulnerabilities registered to JVN iPedia.
As for the vulnerabilities added to JVN iPedia in 2025, 15.5 percent are “Critical” (9.0 – 10.0), 33.5 percent are “High” (7.0 – 8.9), 49.4 percent are “Medium” (4.0 – 6.9) and 1.6 percent are “Low” (0.1 – 3.9).
To avoid the threats posed by the known vulnerabilities, both product developers and IT users should pay close attention to vulnerability disclosures and update the software they use to a fixed version or apply a security patch as soon as it becomes available. They can also check JVN iPedia for new vulnerabilities that are in RSS and XML formats (footnote 8).
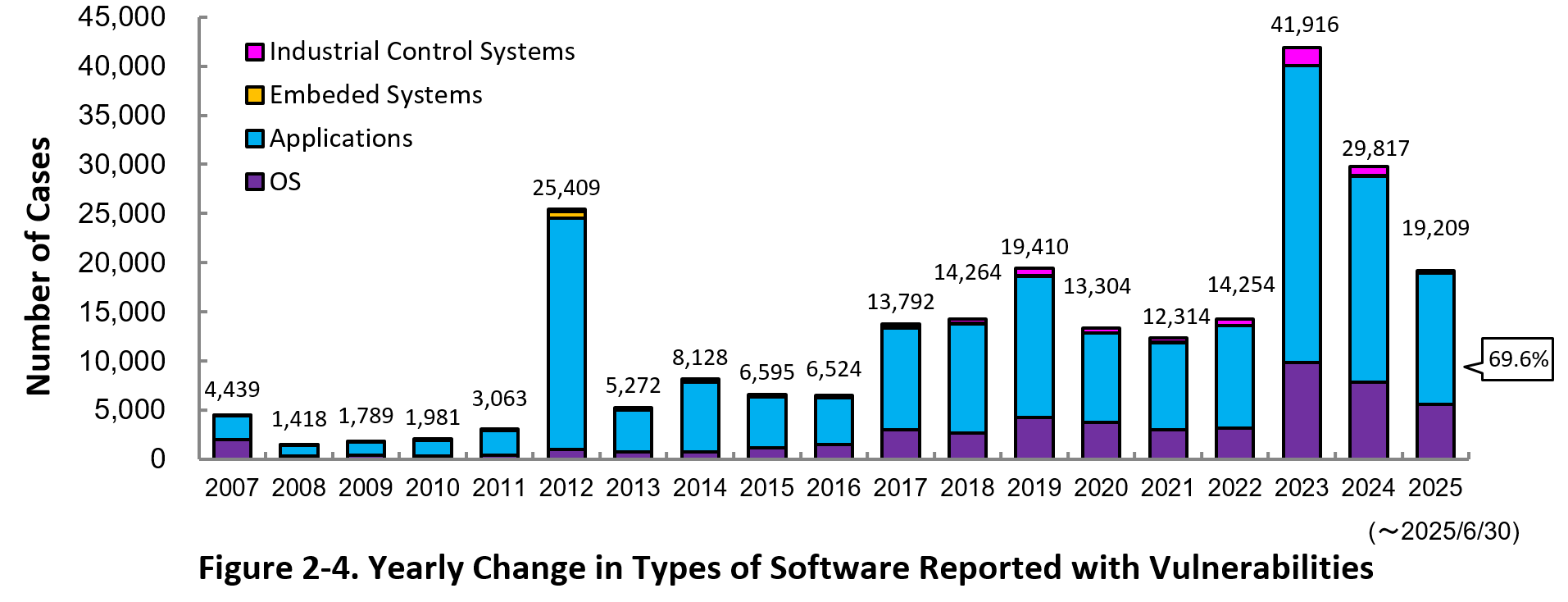
2-3. Types of Software Reported with Vulnerability
Figure 2-4 shows the yearly change in the type of software reported with vulnerability. Application vulnerabilities have been published most, accounting for 69.6 percent (13,378 out of 19,209) of the 2025 total.
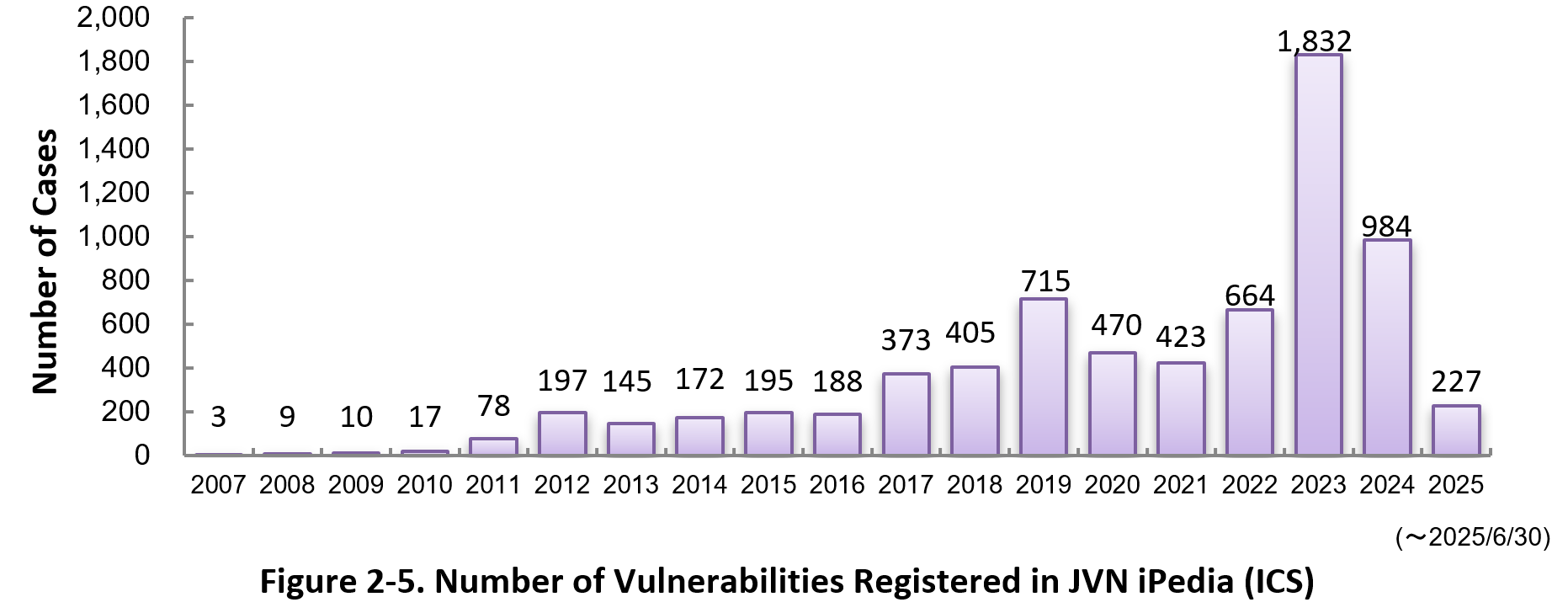
Figure 2-5 shows the yearly change in the number of JVN iPedia-stored vulnerabilities in industrial control systems (ICS) used in critical infrastructure sectors. As of June 2025, the total of 7,107 ICS vulnerabilities have been registered.
2-4. Products Reported with Vulnerability
Table 2-1 lists the top 20 software whose vulnerabilities were most registered to JVN iPedia during the second quarter (April 1 to June 30) of 2025.
This quarter, the most registered products were Qualcomm components, followed by a wide range of operating systems from various vendors, including the Linux kernel, Android, and Apple, and the Adobe Experience Manager content management system.
Besides those in the top 20 list, JVN iPedia stores and offers vulnerability information about a variety of software. IPA hopes software developers and users will make good use of JVN iPedia to efficiently check vulnerability information and take necessary action in a timely manner (footnote 9).
Table 2-1. Top 20 most registered software products vulnerability countermeasure information in JVN iPedia [Apr. – Jun. 2025]
|
Rank
|
Category
|
Product Name (Vendor)
|
Number of
Vulnerabilities Registered |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1
|
Firmware
|
Qualcomm component (Qualcomm) |
657
|
|
2
|
OS
|
Linux Kernel (Linux) |
646
|
|
3
|
OS
|
Android (Google) |
225
|
|
4
|
CMS
|
Adobe Experience Manager (Adobe) |
224
|
|
5
|
OS
|
macOS (Apple) |
217
|
|
6
|
Browser
|
Mozilla Firefox (Mozilla Foundation) |
159
|
|
7
|
OS
|
iPadOS (Apple) |
130
|
|
8
|
OS
|
iOS (Apple) |
121
|
| 9 | Email software | Mozilla Thunderbird (Mozilla Foundation) | 110 |
|
10
|
PDF Viewer/Editor
|
PDF-XChange Editor (PDF-Xchange) |
101
|
|
11
|
OS
|
Debian GNU/Linux (Linux) |
100
|
|
12
|
PDF Viewer/Editor
|
pdf-tools (PDF-Xchange) |
99
|
|
13
|
OS | visionOS (Apple) |
76
|
|
14
|
OS
|
tvOS (Apple) |
71
|
|
15
|
Browser
|
Google Chrome (Google) |
67
|
|
16
|
Middleware | MySQL (Oracle) |
65
|
|
17
|
Business software
|
civil 3d (Autodesk) |
60
|
|
17
|
Business software
|
Advance Steel (Autodesk) |
60
|
| 17 | Business software | AutoCAD Map 3D (Autodesk) | 60 |
|
17
|
Business software
|
AutoCAD MEP (Autodesk) |
60
|
| 17 | Business software | AutoCAD (Autodesk) | 60 |
| 17 | Business software | AutoCAD Plant 3D (Autodesk) | 60 |
| 17 | Business software | AutoCAD Mechanical (Autodesk) | 60 |
3. Most Accessed Vulnerability Countermeasure Information
Table 3-1 lists the top 20 most accessed vulnerability countermeasure information in JVN iPedia during the second quarter (April 1 to June 30) of 2025.
This quarter, all of the top 20 were vulnerability countermeasure information published in Japan Vulnerability Notes (JVN), the vulnerability countermeasure information portal.
Table 3-1. Top 20 Most Accessed Vulnerability Countermeasure Information in JVN iPedia [Apr. – Jun. 2025]
|
Rank
|
ID/Title
|
CVSSv2
Base Score
|
CVSSv3
Base Score
|
Publication Date
|
Access Count |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1
|
-
|
6.3
|
2025/4/1
|
8,279
|
|
|
2
|
-
|
4.3
|
2025/2/4
|
6,113
|
|
|
3
|
JVNDB-2025-000006
|
-
|
4.8
|
2025/1/28
|
5,954
|
|
4
|
JVNDB-2025-000027
Active! mail vulnerable to stack-based buffer overflow |
-
|
9.8
|
2025/4/18
|
5,282
|
|
5
|
-
|
5.3
|
2024/6/19
|
5,247
|
|
|
6
|
-
|
5.4
|
2024/9/4
|
5,223
|
|
|
7
|
-
|
4.8
|
2024/11/13
|
5,131
|
|
|
8
|
-
|
4.8
|
2024/12/16
|
5,096
|
|
|
9
|
-
|
4.3
|
2024/6/26
|
5,081
|
|
|
10
|
-
|
4.7
|
2024/6/7
|
5,034
|
|
|
11
|
JVNDB-2024-000097
WordPress Plugin "Forminator" vulnerable to cross-site scripting |
-
|
6.1
|
2024/9/9
|
5,033
|
|
12
|
JVNDB-2024-000038
Multiple vulnerabilities in WordPress Plugin "Ninja Forms" |
-
|
5.4
|
2024/4/8
|
5,013
|
|
13
|
JVNDB-2024-000100
Multiple vulnerabilities in WordPress plugin "Welcart e-Commerce" |
-
|
8.8
|
2024/9/18
|
4,991
|
|
14
|
JVNDB-2024-000041
Multiple vulnerabilities in WordPress Plugin "Forminator" |
-
|
9.8
|
2024/4/18
|
4,980
|
|
15
|
7.5
|
8.3
|
2023/5/15
|
4,974
|
|
|
16
|
-
|
5.4
|
2024/5/8
|
4,965
|
|
|
17
|
2.6
|
4.3
|
2024/3/25
|
4,963
|
|
|
18
|
3.5
|
5.4
|
2023/8/21
|
4,955
|
|
|
18
|
-
|
2.7
|
2024/5/17
|
4,955
|
|
|
20
|
-
|
4.8
|
2024/11/26
|
4,939
|
Table 3-2 lists the top 5 most accessed vulnerability information among those reported by domestic software developers.
Table 3-2. Top 5 Most Accessed Vulnerabilities Reported by Domestic Product Developers [Apr. – Jun. 2025]
|
Rank
|
ID/Title
|
CVSSv2
Base Score
|
CVSSv3
Base Score
|
Publication Date
|
Access Count |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1
|
JVNDB-2025-001244
|
-
|
-
|
2025/1/30
|
1,867
|
|
2
|
-
|
9.4
|
2024/12/17
|
1,139
|
|
|
3
|
-
|
-
|
2024/9/11
|
1,084
|
|
|
4
|
JVNDB-2024-009498
|
-
|
-
|
2024/10/1
|
819
|
|
5
|
-
|
7.8
|
2024/8/27
|
714
|
Footnotes
(1) Japan Vulnerability Notes: A portal for vulnerability countermeasure information including information on vendor response to the reported vulnerabilities and security support. Operated in the collaboration of IPA and JPCERT/CC.
(2) National Vulnerability Database: A vulnerability database operated by NIST.
(3) National Institute of Standards and Technology: A U.S federal agency that develops and promotes measurement, standards and technology.
(4) Vulnerability Countermeasure Guide for Software Developers (in Japanese only)
(5) How to Secure Your Websites (latest version in Japanese only)
(6) AppGoat (in Japanese only)
(7) NIST - "Retirement of CVSS v2"
(8) IPA Data Feeds (in Japanese only)
(9) IPA Technical Watch - Daily Practice Guide (in Japanese only): Tips on Vulnerability Management The guide gives tips on how to efficiently collect and leverage vulnerability information.
Past Quarterly Reports
Contact information
IT Security Center,
Information-technology Promotion Agency, Japan (ISEC/IPA)