Enhancing information security

Vulnerability Countermeasure Information Database JVN iPedia Registration Status [2018 3rd Quarter (Jul. - Sep.)]
Release Date:Nov 6, 2018
IT Security Center
1. 2018 3rd Quarter: Vulnerability Countermeasure Information Database JVN iPedia Registration Status
The vulnerability countermeasure information database JVN iPedia (https://jvndb.jvn.jp/en/) is endeavoring to become a comprehensive vulnerability database where vulnerability information is aggregated for easy access for IT users. JVN iPedia collects and/or translates the vulnerability information published by 1) domestic software developers, 2) JVN (*1), a vulnerability information portal run by JPCERT/CC and IPA, and 3) NVD (*2), a vulnerability database run by NIST (*3). JVN iPedia has been making vulnerability information available to the public since April 25, 2007.
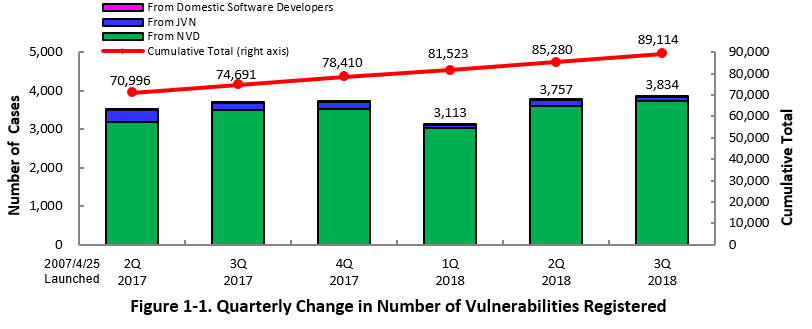
1-1. Vulnerabilities Registered in 2018/3Q
~ JVN iPedia now stores 89,114 vulnerabilities ~
The summary of the vulnerability information registered to the Japanese version of JVN iPedia during the 3rd quarter of 2018 (July 1 to September 30, 2018) is shown in the table below. As of the end of September 2018, the total number of vulnerabilities stored in JVN iPedia is 89,114 (Table 1-1, Figure 1-1).
As for the English version, the total of 1,955 vulnerabilities are available as shown in the lower half of the table.
Table 1-1. Registered Vulnerabilities in 3rd Quarter of 2018
|
|
Information Source
|
Registered Cases
|
Cumulative Cases
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Japanese Version
|
Domestic Software Developers
|
3 cases
|
204 cases
|
|
JVN
|
106 cases
|
8,205 cases
|
|
|
NVD
|
3,725 cases
|
80,705 cases
|
|
|
Total
|
3,834 cases
|
89,114 cases
|
|
|
English Version
|
Domestic Software Developers
|
3 cases
|
204 cases
|
|
JVN
|
30 cases
|
1,751 cases
|
|
|
Total
|
33 cases
|
1,955 cases
|
2. Details on JVN iPedia Registered Data
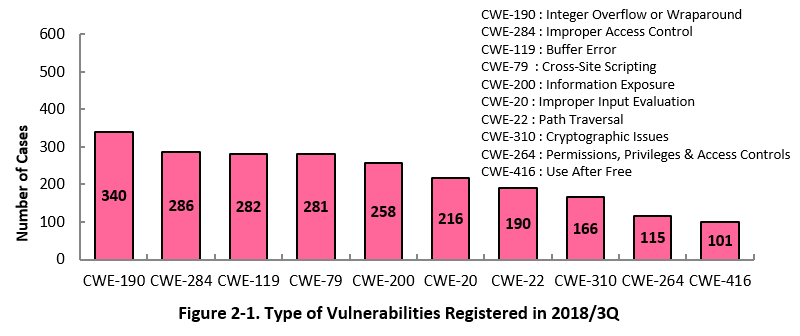
2-1. Types of Vulnerabilities Reported
Figure 2-1 shows the number of vulnerabilities newly added to JVN iPedia during the 3rd quarter of 2018, sorted by the CWE vulnerability types.
The type of the vulnerabilities reported most in the 3rd quarter is CWE-190 (Integer Overflow or Wraparound) with 340 cases, followed by CWE-284 (Improper Access Control) with 286, CWE-119 (Buffer Error) with 282, CWE-79 (Cross-Site Scripting) with 281, CWE-200 (Information Exposure) with 258.
If exploited to cause buffer overflow, CWE-190, the most reported vulnerability type this quarter, could allow attackers to change data on memory supposed to be inaccessible, which may result in undesired consequences, such as crash of a program or arbitrary code execution.
Software developers need to make sure to implement necessary security controls from the planning and design phase of software development to mitigate vulnerability. IPA provides tools and guidelines, such as "How to Secure Your Website" (*4), "Secure Programing Guide" (*5) and "AppGoat" (*6), a hands-on venerability learning tool, for website developers and operators to build secure websites.
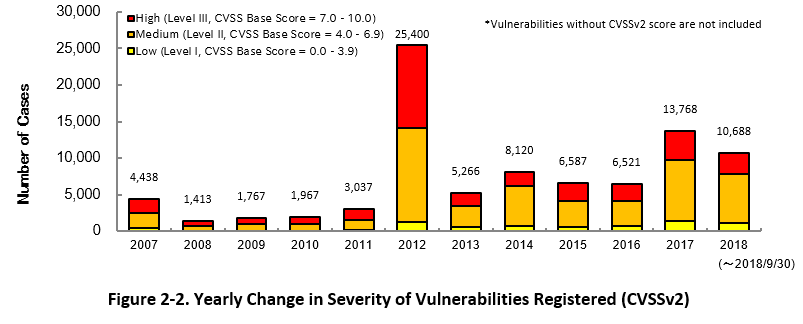
2-2. Severity of Vulnerabilities Reported
Figure 2-2 shows the yearly change in the CVSSv2 rating scale based severity of vulnerabilities registered to JVN iPedia.
As for the vulnerabilities added to JVN iPedia in 2018, 27.1 percent are "level III" (7.0 - 10.0), 62.7 percent are "level ll" (4.0 – 6.9) and 10.2 percent are "level I" (0.0 – 3.9). This means 89.8 percent of all vulnerabilities registered are level II or higher, which are potentially critical enough to cause damage like information exposure or data modification.
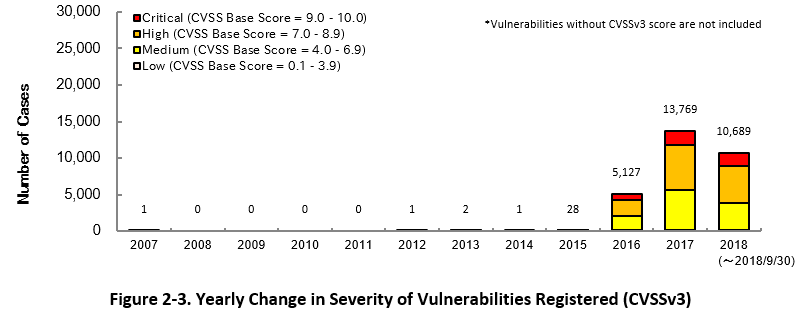
Figure 2-3 shows the yearly change in the CVSSv3 rating scale based severity of vulnerabilities registered to JVN iPedia.
As for the vulnerabilities added to JVN iPedia in 2018, 16.7 percent are "Critical" (9.0 – 10.0), 47.0 percent are "High" (7.0 – 8.9), 35.1 percent are "Medium" (4.0 – 6.9) and 1.2 percent are "Low" (0.1 – 3.9).
To mitigate threats imposed by the known vulnerabilities, IT users should pay close attention to vulnerability information and update software they use to a fixed version or apply a security patch as soon as possible when they become available. IT users can check vulnerabilities newly published on JVN iPedia in RSS and XML format (*7) as well.
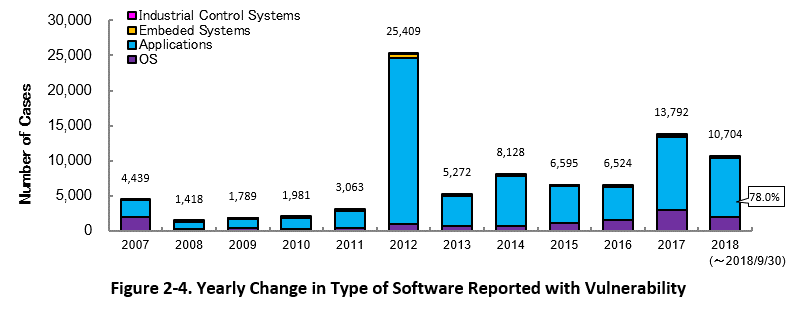
2-3. Types of Software Reported with Vulnerability
Figure 2-4 shows the yearly change in the type of software reported with vulnerability. Application vulnerabilities have been published most, accounting for 78.0 percent (8,353 out of 10,704) of the 2018 total.
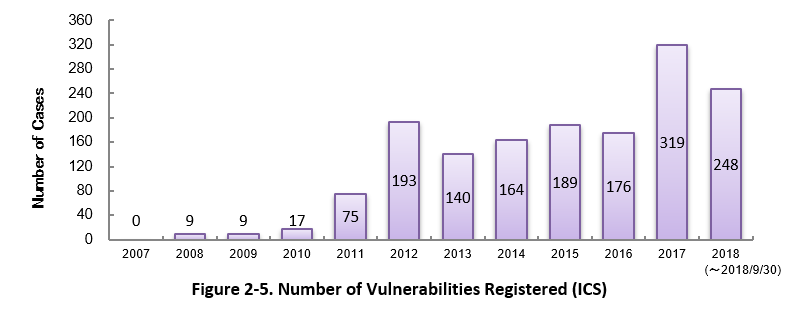
Figure 2-5 shows the yearly change in the number of JVN iPedia-stored vulnerabilities in industrial control systems (ICS) used in critical infrastructure sectors. As of September 2018, the total of 1,539 ICS vulnerabilities have been registered.
2-4. Products Reported with Vulnerability
Table 2-1 lists the top 20 software whose vulnerabilities were most registered to JVN iPedia during the 3rd quarter (July to September) of 2018.
In this quarter, ranked 1st is Mozilla Firefox by Mozilla Foundation. Its Mozilla Thunderbirds and Mozilla Firefox ESR are also ranked 8th and 10th, respectively. Below the 2nd are mostly occupied by OS products, starting with Debian GNU/Linux, and those of Red Hat and Microsoft.
Besides those in the top 20 list, JVN iPedia stores and offers vulnerability information about a variety of software. IPA hopes software developers and users will make good use of JVN iPedia to efficiently check vulnerability information and take necessary action in a timely manner (*8).
Table 2-1. Top 20 Software Products Vulnerabilities Were Most Registered [Jul. – Sep. 2018]
|
Rank
|
Category
|
Product Name (Vendor)
|
Number of
Vulnerabilities Registered |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1
|
Browser
|
Mozilla Firefox (Mozilla Foundation)
|
301
|
|
2
|
OS
|
Debian GNU/Linux (Debian)
|
212
|
|
3
|
PDF Viewer
|
Adobe Acrobat Reader DC (Adobe Systems)
|
155
|
|
3
|
PDF Viewer/Editor
|
Adobe Acrobat (Adobe Systems)
|
155
|
|
3
|
PDF Viewer/Editor
|
Adobe Acrobat DC (Adobe Systems)
|
155
|
|
6
|
OS
|
Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server (Red Hat)
|
153
|
|
7
|
OS
|
Red Hat Enterprise Linux Workstation (Red Hat)
|
152
|
|
8
|
OS
|
Red Hat Enterprise Linux Desktop (Red Hat)
|
150
|
|
8
|
Email Software
|
Mozilla Thunderbird (Mozilla Foundation)
|
150
|
|
10
|
Browser
|
Mozilla Firefox ESR (Mozilla Foundation)
|
149
|
|
11
|
OS
|
Ubuntu (Canonical)
|
144
|
|
12
|
OS
|
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (Red Hat)
|
89
|
|
13
|
OS
|
Android (Google)
|
87
|
|
14
|
Qualiy Management Software
|
Rational Quality Manager (IBM)
|
48
|
|
15
|
Development Management
Software |
Rational Collaborative Lifecycle Management (IBM)
|
40
|
|
15
|
OS
|
Microsoft Windows 10 (Microsoft)
|
40
|
|
17
|
OS
|
Microsoft Windows Server (Microsoft)
|
38
|
|
17
|
OS
|
Linux Kernel (Kernel.org)
|
38
|
|
19
|
OS
|
iOS (Apple)
|
37
|
|
20
|
OS
|
Microsoft Windows Server 2016 (Microsoft)
|
34
|
3. Most Accessed Vulnerability Countermeasure Information
Table 3-1 lists the top 20 most accessed vulnerability information in JVN iPedia during the 3rd quarter of 2018 (July – September).
In this quarter, all top 20 vulnerabilities are those disclosed on the JVN (Japan Vulnerability Notes). Vulnerabilities released on JVN includes those disclosed in accordance with the Information Security Early Warning Partnership (*9). Those vulnerabilities received a lot of attention and picked up by news media and blogs, which probably made the access number up.
Table 3-1. Top 20 Most Accessed Vulnerability Countermeasure Information in JVN iPedia [Jul. – Sep. 2018]
No.1 The installers of multiple Logicool software programs may insecurely load Dynamic Link Libraries JVNDB-2018-000072
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
6.8
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
7.8
- Date Public
-
2018/7/6
- Access Count
-
5,875
No.2 Cybozu Garoon vulnerable to SQL injection JVNDB-2018-000069
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
- Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
6.5
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
6.3
- Date Public
-
2018/7/2
- Access Count
-
5,795
No.3 Multiple OS command injection vulnerabilities in Aterm WG1200HP JVNDB-2018-000075
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
5.2
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
6.8
- Date Public
-
2018/7/12
- Access Count
-
5,617
No.4 DHC Online Shop App for Android fails to verify SSL server certificates JVNDB-2018-000071
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
4.0
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
4.8
- Date Public
-
2018/7/6
- Access Count
-
5,596
No5. Multiple vulnerabilities in Calsos CSDX and CSDJ series products JVNDB-2018-000068
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
6.5
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
8.8
- Date Public
-
2018/7/2
- Access Count
-
5,585
No.6 Installer of Glary Utilities may insecurely load Dynamic Link Libraries JVNDB-2018-000070
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
6.8
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
7.8
- Date Public
-
2018/7/3
- Access Count
-
5,570
No.7 Explzh vulnerable to directory traversal JVNDB-2018-000079
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
4.3
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Low
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
3.3
- Date Public
-
2018/7/13
- Access Count
-
5,473
No.8 Multiple vulnerabilities in Aterm HC100RC JVNDB-2018-000077
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
5.2
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
6.8
- Date Public
-
2018/7/12
- Access Count
-
5,412
No.9 Multiple vulnerabilities in Aterm W300P JVNDB-2018-000076
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
5.2
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
6.8
- Date Public
-
2018/7/12
- Access Count
-
5,238
No.10 Movable Type plugin MTAppjQuery vulnerable to PHP code execution JVNDB-2018-000080
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level III (High)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
7.5
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
7.3
- Date Public
-
2018/7/18
- Access Count
-
5,166
No.11 Multiple vulnerabilities in ORCA (Online Receipt Computer Advantage) JVNDB-2018-000081
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
5.2
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
5.5
- Date Public
-
2018/7/18
- Access Count
-
5,164
No.12 Mailman vulnerable to cross-site scripting JVNDB-2018-000067
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
4.0
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
4.8
- Date Public
-
2018/6/28
- Access Count
-
5,139
No.13 Multiple directory traversal vulnerabilities in AttacheCase JVNDB-2018-000090
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
4.3
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Low
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
3.3
- Date Public
-
2018/8/6
- Access Count
-
5,092
No.14 WordPress plugin "FV Flowplayer Video Player" vulnerable to cross-site scripting JVNDB-2018-000078
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level I (Low)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
2.6
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
6.1
- Date Public
-
2018/7/17
- Access Count
-
5,060
No.15 The installers of multiple Canon IT Solutions Inc. software programs may insecurely load Dynamic Link Libraries JVNDB-2018-000083
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
6.8
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
7.8
- Date Public
-
2018/7/24
- Access Count
-
4,981
No.16 MemoCGI vulnerable to directory traversal JVNDB-2018-000066
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
5.0
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
5.8
- Date Public
-
2018/6/27
- Access Count
-
4,980
No.17 EC-CUBE vulnerable to session fixation JVNDB-2018-000035
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
5.8
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
4.2
- Date Public
-
2018/4/17
- Access Count
-
4,826
No.18 DLL planting vulnerability in multiple Yayoi 17 Series products JVNDB-2018-000074
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
6.8
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
7.8
- Date Public
-
2018/7/20
- Access Count
-
4,817
No.19 LINE MUSIC for Android fails to verify SSL server certificates JVNDB-2018-000084
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
4.0
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
4.8
- Date Public
-
2018/7/26
- Access Count
-
4,807
No.20 WL-330NUL vulnerable to cross-site request forgery JVNDB-2018-000082
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level I (Low)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
2.6
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
4.3
- Date Public
-
2018/7/20
- Access Count
-
4,727
Table 3-2 lists the top 5 most accessed vulnerability information among those reported by domestic software developers.
Table 3-2. Top 5 Most Accessed Vulnerabilities Reported by Domestic Software Developers [Jul. - Sep. 2018]
No.1 Access Control Vulnerability in Hitachi Infrastructure Analytics Advisor JVNDB-2018-003030
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level III (High)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
7.5
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
7.3
- Date Public
-
2018/5/10
- Access Count
-
4,224
No.2 Cross-site Scripting Vulnerability in Fujitsu Interstage List Works JVNDB-2017-004687
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
4.3
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
6.1
- Date Public
-
2017/7/5
- Access Count
-
3,928
No.3 XXE Vulnerability in Hitachi Device Manager JVNDB-2018-001389
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level III (High)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
7.8
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
7.4
- Date Public
-
2018/2/14
- Access Count
-
3,919
No.4 DoS Vulnerability in JP1/ServerConductor/Deployment Manager and Hitachi Compute Systems Manager JVNDB-2018-002257
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level III (High)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
7.8
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
7.5
- Date Public
-
2018/4/4
- Access Count
-
3,914
No.5 Cross-site Scripting Vulnerability in Fujitsu NetCOBOL JVNDB-2017-010236
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
3.5
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
4.8
- Date Public
-
2017/12/8
- Access Count
-
3,871
Footnotes
-
(*1)
-
(*2)
-
(*3)
-
(*4)
-
(*5)
-
(*6)
-
(*7)
-
(*8)
-
(*9)
Past Quarterly Reports
Contact information
IT Security Center,
Information-technology Promotion Agency, Japan (ISEC/IPA)