Enhancing information security

Vulnerability Countermeasure Information Database JVN iPedia Registration Status [2019 4th Quarter (Oct. - Dec.)]
Release Date:Feb 19, 2020
IT Security Center
1. 2019 4th Quarter: Vulnerability Countermeasure Information Database JVN iPedia Registration Status
The vulnerability countermeasure information database JVN iPedia (https://jvndb.jvn.jp/en/) is endeavoring to become a comprehensive vulnerability database where vulnerability information is aggregated for easy access for IT users. JVN iPedia collects and/or translates the vulnerability information published by 1) domestic software developers, 2) JVN (*1), a vulnerability information portal run by JPCERT/CC and IPA, and 3) NVD (*2), a vulnerability database run by NIST (*3). JVN iPedia has been making vulnerability information available to the public since April 25, 2007.
1-1. Vulnerabilities Registered in 2019/4Q
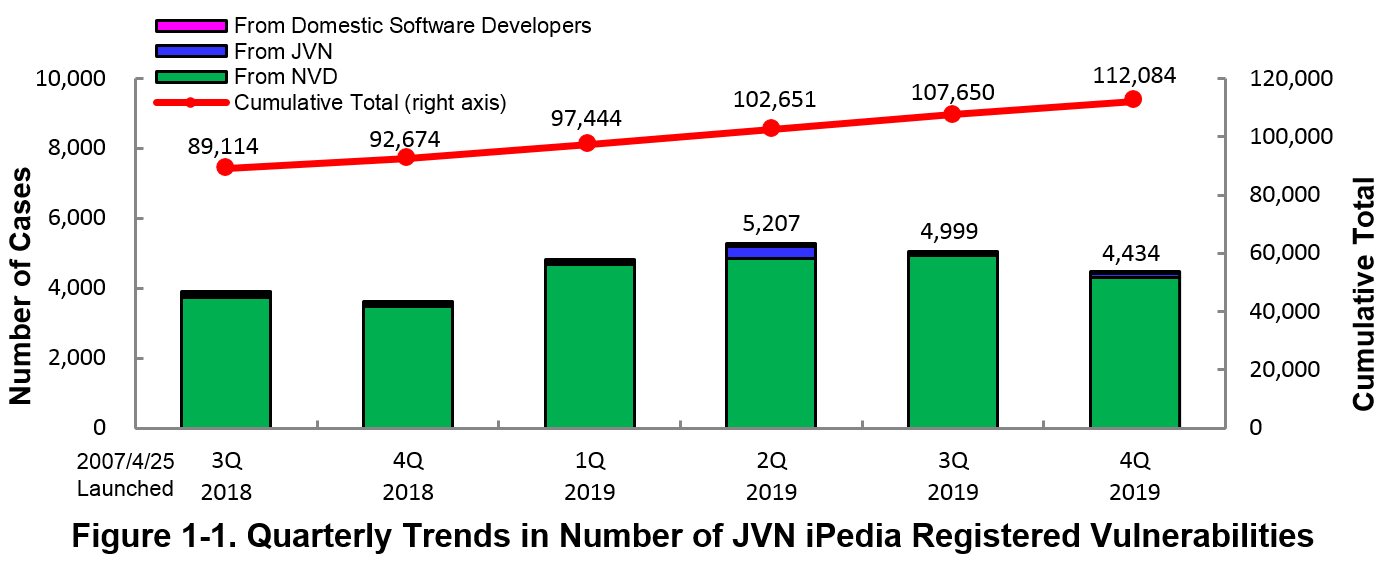
~ JVN iPedia now stores 112,084 vulnerabilities ~
The summary of the vulnerability information registered to the Japanese version of JVN iPedia during the 4th quarter of 2019 (October 1 to December 31, 2019) is shown in the table below. As of the end of December 2019, the total number of vulnerabilities stored in JVN iPedia is 112,084 (Table 1-1, Figure 1-1).
As for the JVN iPedia English version, the total number of vulnerabilities stored is 2,093 as shown in the lower half of the Table 1-1.
Table 1-1. Vulnerabilities Registered to JVN iPedia during 4th Quarter of 2019
|
|
Information Source
|
Registered Cases
|
Cumulative Cases
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Japanese Version
|
Domestic Product Developers
|
8 cases
|
226 cases
|
|
JVN
|
113 cases
|
8,875 cases
|
|
|
NVD
|
4,313 cases
|
102,983 cases
|
|
|
Total
|
4,434 cases
|
112,084 cases
|
|
|
English Version
|
Domestic Product Developers
|
8 cases
|
226 cases
|
|
JVN
|
19 cases
|
1,867 cases
|
|
|
Total
|
27 cases
|
2,093 cases
|
1-2. 【Observation 1】Vulnerabilities in Adobe Flash Player
~ Registered 10 vulnerability countermeasure information with high severity level in 2019, consider migrating to alternative products by the end of support ~
On December 31, 2020, Adobe Systems will officially stop supporting, updating and distributing Adobe Flash Player(*4).
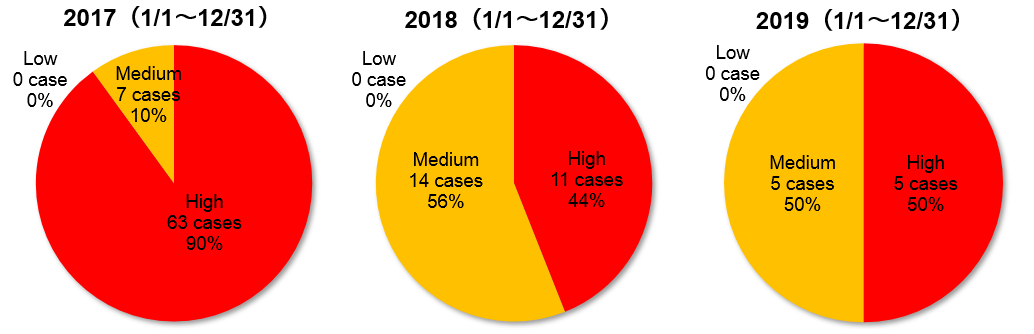
Figure 1-2 shows the percentage of severity of vulnerability information for Adobe Flash Player registered in JVN iPedia from 2017 to 2019. All vulnerabilities registered in the last three years are classified as the highest severity “High” (Level III, CVSS Base Score=7.0–10.0) or the next “Medium” (Level II, CVSS Base Score =4.0-6.9). The result indicates that the registered vulnerabilities are dominated by high severity vulnerabilities.
As for the number of registrations, 70 cases in 2017, 25 in 2018, and 10 in 2019, indicates decreasing trend. However, looking at the percentage of severity classified as “High”, it fluctuated widely, 90% in 2017, 44% in 2018, and 50% in 2019. Although 2017 is prominent, the proportion of high severity vulnerabilities is still high in 2019. The number of registrations is expected to decrease in the future, but the vulnerability information with high severity level is likely to be disclosed.
-

Figure 1-2. Severity of Vulnerability Information for Adobe Flash Player registered in JVN iPedia from 2017 to 2019(CVSSv2)
Generally, when a new vulnerability is discovered after the end of support, product vendors don't correct it. If you continue to use the support ended product, your risk of damage by the attack exploiting the vulnerability increase. It is recommended that organizations publicizing contents which use Adobe Flash Player take measures such as moving to alternative methods (i.e. HTML5). In addition, please inform the content users of how to migrate etc. Migration and notice should be done by the end of support, at the end of 2020.
IPA operates the cyber security alert service “icat (Flash version)” that uses Adobe Flash Player. The service will be ended before the end of 2020 when Adobe support ends and it will be unified to "icat for JSON" (IPA Cyber security Alert Service for JavaScript Object Notation) that does not use Adobe Flash Player(*5). As announced on the website, users of "icat (Flash version)" should migrate to "icat for JSON".
1-3. 【Observation 2】Vulnerabilities related to Remote Desktop Services
~ 63% of vulnerabilities related to Remote Desktop Services is “High” severity level ~
Microsoft released a security notice (CVE-2019-0708) of vulnerability of Remote Desktop Services, called "Bluekeep", in May, 2019(*6). Since the vulnerability allows unauthenticated attackers to execute attack via Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) without any manipulation of the target system, they could be infected by self-propagating worms which could spread on the network, like "WannaCry" which wrecked havoc in 2017. In response to the vulnerability, Microsoft took exceptional measures of releasing patches for support ended OS, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003, in addition to security notice(*7). In November, 2019, the attack which abuses this vulnerability trying to execute crypto currency mining was confirmed. Paying close attention is required for some time in the future(*8).
In 2019, in addition to BlueKeep, Microsoft also disclosed vulnerabilities related to Remote Desktop Services and RDP used to connect them.
Figure 1-3 shows percentage of severity of vulnerability countermeasure information related to Remote Desktop Services and RDP registered to JVN iPedia in 2019 (Jan.1 - Dec. 31).
Table 1-2 is a list of those vulnerabilities. 12 out of 19 cases of disclosed vulnerability countermeasure information are classified as "High" and dominate 63% of all. Rest of 7 cases are "Medium" and there was no "Low" assigned case. CVSS basic score of "Bluekeep" (JVNDB-2019-003551)is 10.0 and classified as "High".
There is a tendency that registered vulnerabilities related to Remote Desktop Services and RDP in 2019 have high severity which contains CVSS base score 10.0.
-
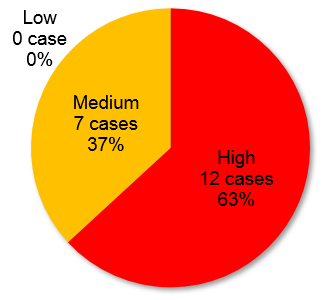
Figure 1-3. Severity of vulnerability countermeasure information(CVSSv2)related to Remote Desktop Services and RDP registered to JVN iPedia in 2019 (Jan.1 - Dec. 31) -

Table 1-2. Vulnerability countermeasure information(CVSSv2)related to Remote Desktop Services and RDP registered to JVN iPedia in 2019 (Jan.1 - Dec. 31)
No.1 Vulnerabilities of DoS in Remote Desktop Protocol of Microsoft Windows Products JVNDB-2019-012975
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
5.0
No.2 Vulnerabilities of information disclosure in Microsoft Windows XP JVNDB-2019-012905
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
5.0
No.3 Vulnerabilities of remote code execution in Windows Remote Desktop Client of Microsoft Windows products JVNDB-2019-010491
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level III (High)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
9.3
No.4 Vulnerabilities of DoS in Remote Desktop Protocol of Microsoft Windows Products JVNDB-2019-010476
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level III (High)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
7.8
No.5 Vulnerabilities of remote code execution in Windows Remote Desktop Client of Microsoft Windows products JVNDB-2019-009253
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level III (High)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
9.3
No.6 Vulnerabilities of remote code execution in Windows Remote Desktop Client of Microsoft Windows products JVNDB-2019-009252
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level III (High)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
9.3
No.7 Vulnerabilities of remote code execution in Windows Remote Desktop Client of Microsoft Windows products JVNDB-2019-009209
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level III (High)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
9.3
No.8 Vulnerabilities of remote code execution in Windows Remote Desktop Client of Microsoft Windows products JVNDB-2019-009208
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level III (High)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
9.3
No.9 Vulnerabilities of information disclosure in Microsoft Windows products JVNDB-2019-008030
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
5.0
No.10 Vulnerabilities of information disclosure in Microsoft Windows products JVNDB-2019-008029
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
5.0
No.11 Vulnerabilities of DoS in Remote Desktop Protocol of Microsoft Windows Products JVNDB-2019-008028
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
5.0
No.12 Vulnerabilities of remote code execution in Remote Desktop Services of Microsoft Windows products JVNDB-2019-007743
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level III (High)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
10.0
No.13 Vulnerabilities of remote code execution in Remote Desktop Services of Microsoft Windows products JVNDB-2019-007742
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level III (High)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
9.3
No.14 Vulnerabilities of remote code execution in Remote Desktop Services of Microsoft Windows products JVNDB-2019-007739
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level III (High)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
10.0
No.15 Vulnerabilities of remote code execution in Remote Desktop Services of Microsoft Windows products JVNDB-2019-007738
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level III (High)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
10.0
No.16 Vulnerabilities of remote code execution in Remote Desktop Services of Microsoft Windows products JVNDB-2019-006521
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level III (High)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
8.5
No.17 Vulnerabilities of information disclosure in Microsoft Windows products JVNDB-2019-006364
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
4.0
No.18 Microsoft Windows Remote Desktop Network Level Authentication Bypass Windows Lockscreen JVNDB-2019-004672
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
4.6
No.19 Vulnerabilities of remote code execution in Remote Desktop Services of Microsoft Windows products JVNDB-2019-003551
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level III (High)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
10.0
People working in organizations use Remote Desktop Services to access other devices in some cases. Since Remote Desktop Services is one of the Windows standard functions, when the device is shared, the function may being set effective unintentionally.
Remote Desktop Services is very useful, but it may cause huge damage or disruption when abused. It is recommended to apply security patch as soon as they become available.
2. Details on JVN iPedia Registered Data
2-1. Types of Vulnerabilities Reported
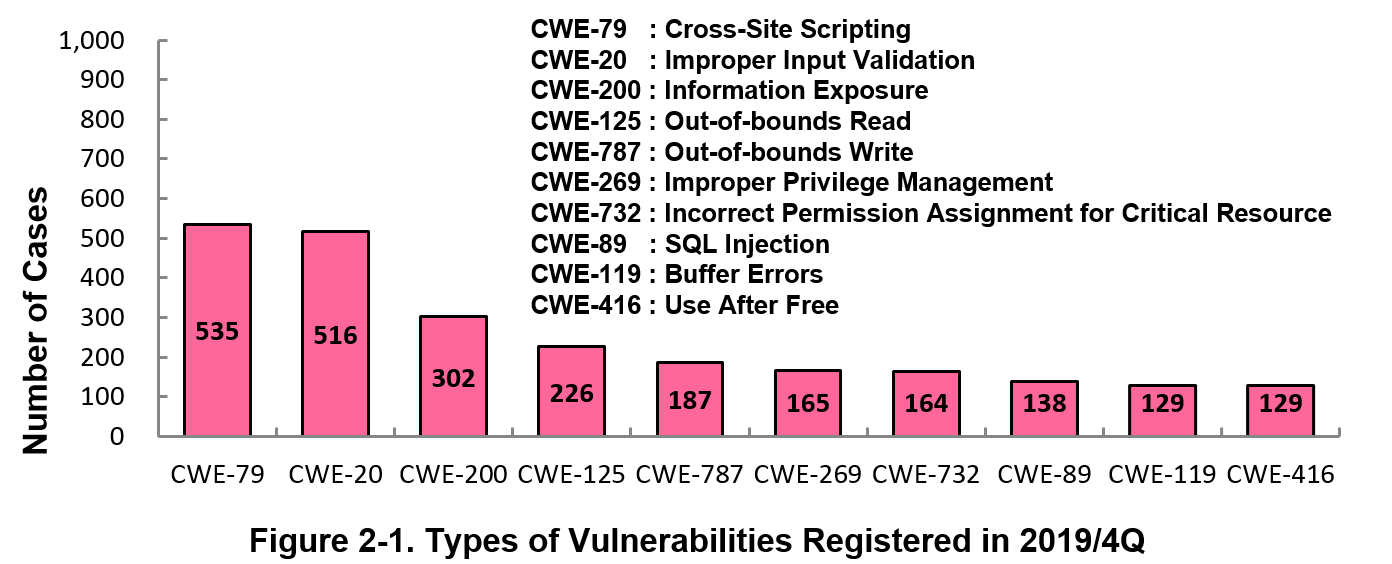
Figure 2-1 shows the number of vulnerabilities newly added to JVN iPedia during the 4th quarter of 2019, sorted by the CWE vulnerability types.
The type of the vulnerabilities reported most in the 4th quarter is CWE-79 (Cross-Site Scripting) with 535 cases, followed by CWE-20 (Improper Input Validation) with 516, CWE-200 (Information Exposure) with 302, CWE-125 (Out-of-bounds Read) with 226, CWE-787 (Out-of-bounds Write) with 187.
CWE-79 (Cross-Site Scripting), the most reported vulnerability type in this quarter, could allow attackers to display false webpages and/or steal information.
Software developers need to make sure to mitigate vulnerability from the planning and design phase of software development. IPA provides tools and guidelines, such as "How to Secure Your Website" (*9), "Secure Programing Guide" (*10) and "AppGoat" (*11), a hands-on venerability learning tool, for website developers and operators to build secure websites.
2-2. Severity of Vulnerabilities Reported
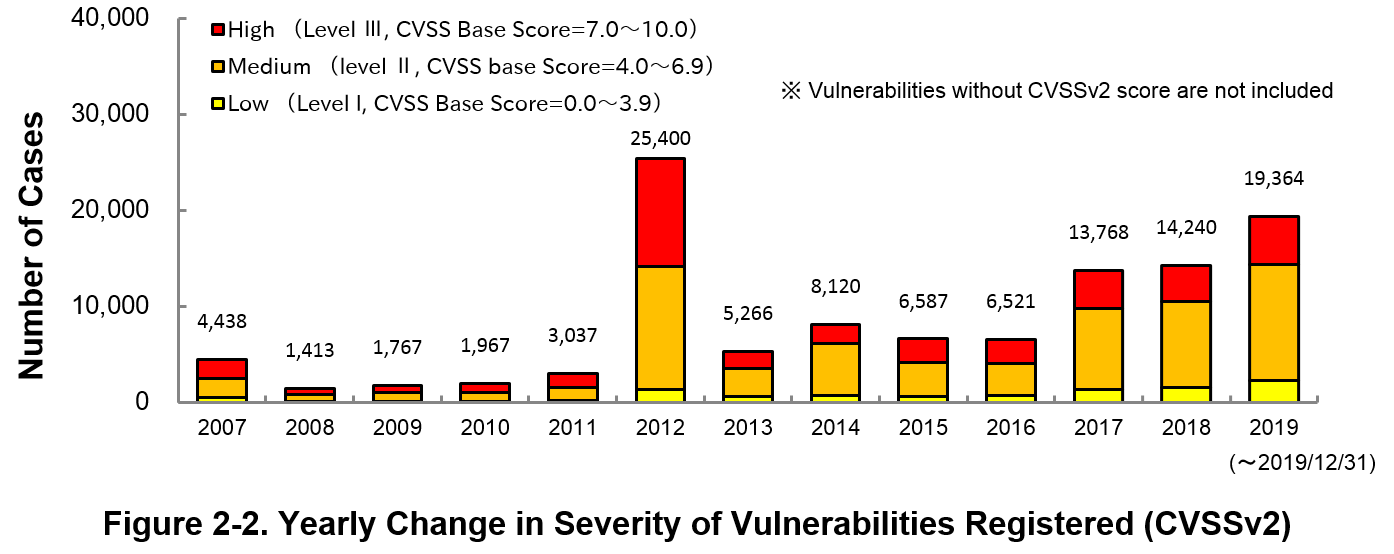
Figure 2-2 shows the yearly change in the CVSSv2 rating scale based severity of vulnerabilities registered to JVN iPedia.
As for the vulnerabilities added to JVN iPedia in 2019, 25.8 percent are “Level III” (7.0 - 10.0), 62.7 percent are “Level ll” (4.0 – 6.9) and 11.5 percent are “Level I” (0.0 – 3.9). This means 88.5 percent of all vulnerabilities registered are Level II or higher, which are potentially critical enough to cause damage like information exposure or data falsification.
Figure 2-3 shows the yearly change in the CVSSv3 rating scale based severity of vulnerabilities registered to JVN iPedia.
As for the vulnerabilities added to JVN iPedia in 2019, 15.8 percent are “Critical” (9.0 – 10.0), 41.9 percent are “High” (7.0 – 8.9), 40.7 percent are “Medium” (4.0 – 6.9) and 1.6 percent are “Low” (0.1 – 3.9).
To avoid threats posed by the known vulnerabilities, both product developers and IT users should pay close attention to vulnerability disclosure and [strong]update software they use to a fixed version or apply a security patch[/strong] as soon as possible when they become available. IT users can check vulnerabilities newly published on JVN iPedia in RSS and XML format (*12) as well.
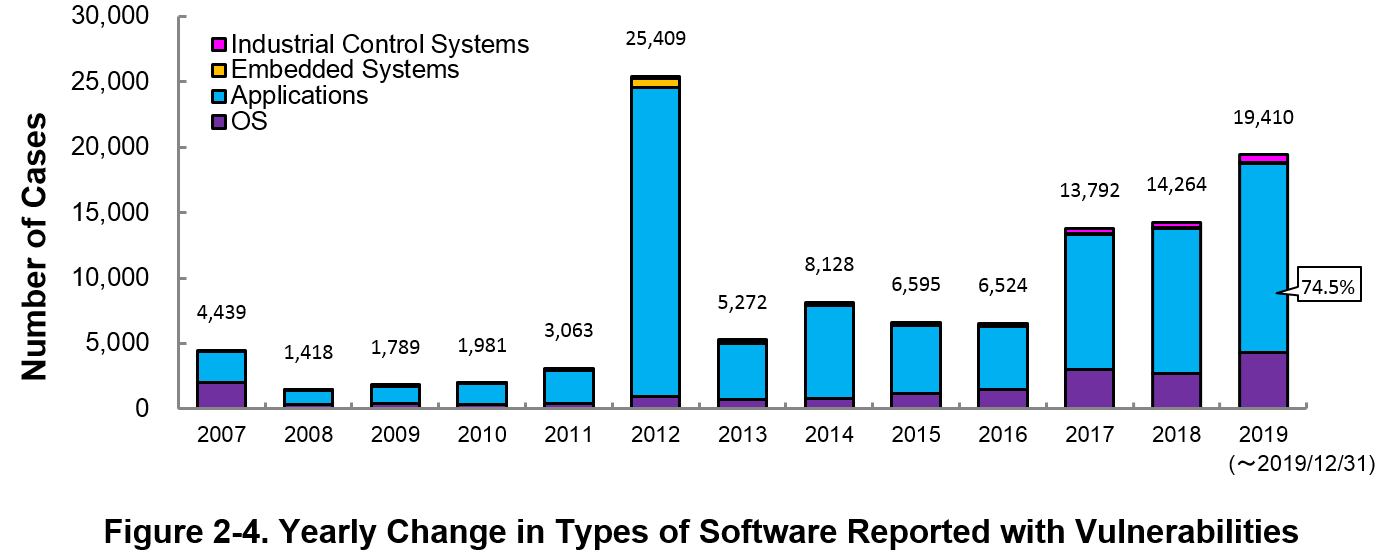
2-3. Types of Software Reported with Vulnerability
Figure 2-4 shows the yearly change in the type of software reported with vulnerability. Application vulnerabilities have been published most, accounting for 74.5 percent (14,470 out of 19,410) of the 2019 total.
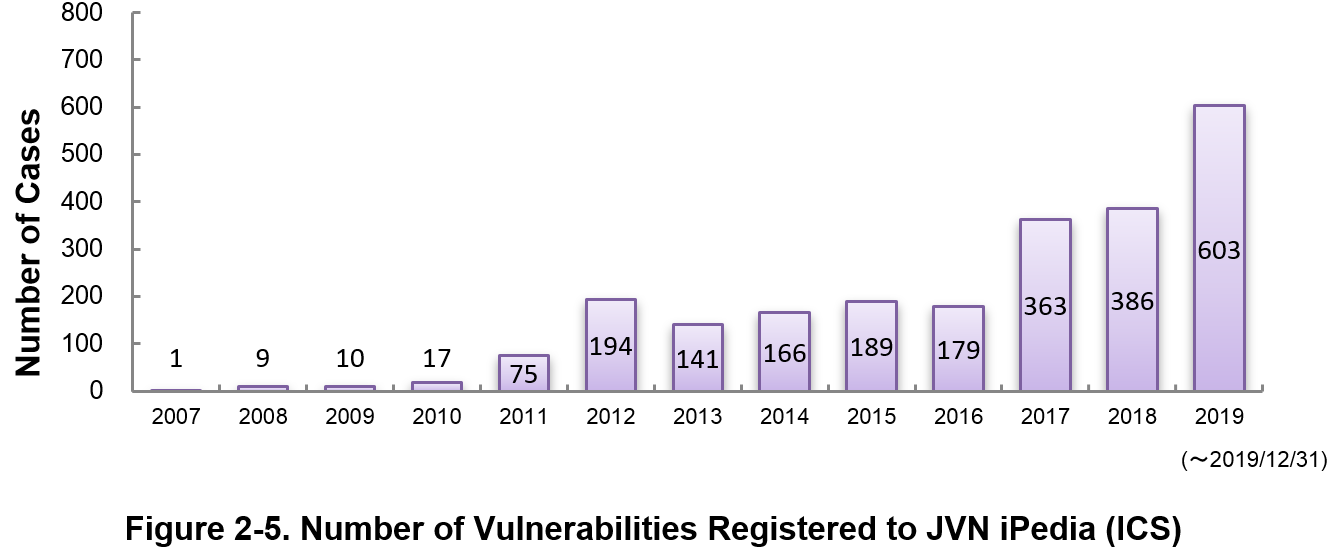
Figure 2-5 shows the yearly change in the number of JVN iPedia-stored vulnerabilities in industrial control systems (ICS) used in critical infrastructure sectors. As of December 2019, the total of 2,333 ICS vulnerabilities have been registered.
2-4. Products Reported with Vulnerability
Table 2-1 lists the top 20 software whose vulnerabilities were most registered to JVN iPedia during the 4th quarter (October to December) of 2019.
In this quarter, Android OS with 315 cases is the 1st rank. From 2nd to 20th, various OS products are ranked, such as Microsoft Windows products, Linux OS (Debian GNU/Linux, Linux Kernel).
Besides those in the top 20 list, JVN iPedia stores and offers vulnerability information about a variety of software. IPA hopes software developers and users will make good use of JVN iPedia to efficiently check vulnerability information and take necessary action in a timely manner (*13)
.
Table 2-1. Top 20 Software Products Vulnerabilities Were Most Registered [Oct. – Dec. 2019]
|
Rank
|
Category
|
Product Name (Vendor)
|
Number of
Vulnerabilities Registered |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1
|
OS
|
Android (Google)
|
315
|
|
2
|
OS
|
Debian GNU/Linux (Debian)
|
225
|
|
3
|
Browser
|
Google Chrome (Google)
|
154
|
|
4
|
OS
|
Linux Kernel (Kernel.org)
|
118
|
|
5
|
OS
|
Fedora (Fedora Project)
|
99
|
|
6
|
OS
|
Microsoft Windows 10 (Microsoft)
|
97
|
|
7
|
OS
|
Microsoft Windows Server (Microsoft)
|
92
|
|
7
|
Firmware
|
Qualcomm component (Qualcomm)
|
92
|
|
9
|
OS
|
Microsoft Windows Server 2019 (Microsoft)
|
88
|
|
10
|
OS
|
Microsoft Windows Server 2016 (Microsoft)
|
72
|
|
11
|
PDF Viewer
|
Adobe Acrobat Reader DC (Adobe Systems)
|
70
|
|
11
|
PDF Viewer/Editor
|
Adobe Acrobat DC (Adobe Systems)
|
70
|
|
13
|
CMS
|
Magento (Magento, Inc.)
|
65
|
|
13
|
OS
|
Microsoft Windows 7 (Microsoft)
|
65
|
|
15
|
OS
|
Microsoft Windows 8.1 (Microsoft)
|
64
|
|
15
|
OS
|
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 (Microsoft)
|
64
|
|
17
|
OS
|
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 (Microsoft)
|
63
|
|
18
|
OS
|
Microsoft Windows RT 8.1 (Microsoft)
|
60
|
|
19
|
OS
|
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (Red Hat)
|
53
|
|
20
|
OS
|
Ubuntu (Canonical)
|
38
|
3. Most Accessed Vulnerability Countermeasure Information
Table 3-1 lists the top 20 most accessed vulnerability countermeasure information in JVN iPedia during the 4th quarter of 2019 (October to December).
All the vulnerability countermeasure information ranked top 20 in this quarter are vulnerability countermeasure information released on the Vulnerability Countermeasure Information Portal Site JVN.
Rating Scale
Note 1) CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
- Level I (Low)
- CVSS Base Score = 0.0~3.9
- Level II (Medium)
- CVSS Base Score = 4.0~6.9
- Level III (High)
- CVSS Base Score = 7.0~10.0
Note 2) CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
- Low
- CVSS Base Score =0.1~3.9
- Medium
- CVSS Base Score =4.0~6.9
- High
- CVSS Base Score =7.0~8.9
- Critical
- CVSS Base Score =9.0~10.0
Table 3-1. Top 20 Most Accessed Vulnerability Countermeasure Information in JVN iPedia [Oct. – Dec. 2019]
No.1 Multiple integer overflow vulnerabilities in LINE(Android) JVNDB-2019-000060
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
- Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
6.8
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
- Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
6.3
- Date Public
-
2019/9/19
- Access Count
-
9,135
No.2 Rakuma App vulnerable to authentication information disclosure JVNDB-2019-000068
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
- Level I (Low)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
2.6
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
4.7
- Date Public
-
2019/11/7
- Access Count
-
8,875
No.3 Vulnerability in Cosminexus HTTP Server and Hitachi Web Server JVNDB-2019-010374
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
-
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
-
- Date Public
-
2019/10/11
- Access Count
-
8,116
No.4 Multiple vulnerabilities in WordPress Plugin "wpDataTables Lite" JVNDB-2019-000064
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
6.5
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
7.2
- Date Public
-
2019/10/11
- Access Count
-
8,097
No.5 Multiple vulnerabilities in EC-CUBE module "REMISE Payment module (2.11, 2.12 and 2.13)" JVNDB-2019-000063
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
5.0
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
5.3
- Date Public
-
2019/10/7
- Access Count
-
7,200
No.6 FON routers may behave as an open resolver JVNDB-2019-009884
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
- Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
5.0
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
- Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
5.8
- Date Public
-
2019/10/2
- Access Count
-
7,164
No.7 Multiple OS command injection vulnerabilities in DBA-1510P JVNDB-2019-000062
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
- Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
5.8
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
8.8
- Date Public
-
2019/10/7
- Access Count
-
7,117
No.8 Trend Micro OfficeScan vulnerable to directory traversal JVNDB-2019-011088
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
5.2
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
8.2
- Date Public
-
2019/10/29
- Access Count
-
7,059
No.9 NetCommons3 vulnerable to cross-site scripting
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
4.3
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
6.1
- Date Public
-
2019/10/15
- Access Count
-
6,921
No.10 apng-drawable vulnerable to integer overflow JVNDB-2019-000059
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
6.8
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
5.3
- Date Public
-
2019/9/12
- Access Count
-
6,866
No.11 Cybozu Garoon vulnerable to SQL injection JVNDB-2019-000054
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
- Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
6.5
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
- High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
7.6
- Date Public
-
2019/8/26
- Access Count
-
6,853
No.12 PowerCMS vulnerable to open redirect JVNDB-2019-000066
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
- Level I (Low)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
2.6
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
4.7
- Date Public
-
2019/10/23
- Access Count
-
6,779
No.13 Smart TV Box fails to restrict access permissions JVNDB-2019-000053
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
6.8
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
7.3
- Date Public
-
2019/8/23
- Access Count
-
6,580
No.14 Multiple vulnerabilities in Hikari Denwa router/Home GateWay JVNDB-2019-000043
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
4.3
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
6.1
- Date Public
-
2019/6/27
- Access Count
-
6,575
No.15 Multiple vulnerabilities in VAIO Update JVNDB-2019-000040
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
6.8
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
High
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
7.8
- Date Public
-
2019/6/21
- Access Count
-
6,505
No.16 WordPress Plugin "Category Specific RSS feed Subscription" vulnerable to cross-site request forgery JVNDB-2019-000049
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
- Level I (Low)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
2.6
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
- Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
4.3
- Date Public
-
2019/7/18
- Access Count
-
6,447
No.17 WordPress Plugin "WordPress Ultra Simple Paypal Shopping Cart" vulnerable to cross-site request forgery JVNDB-2019-000048
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
- Level I (Low)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
2.6
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
4.3
- Date Public
-
2019/7/16
- Access Count
-
6,415
No.18 WonderCMS vulnerable to directory traversal JVNDB-2019-007404
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level II (Medium)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
5.5
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
6.4
- Date Public
-
2019/8/9
- Access Count
-
6,402
No.19 Multiple Vulnerabilities in Hitachi Global Link Manager JVNDB-2019-010375
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
-
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
-
- Date Public
-
2019/10/11
- Access Count
-
6,277
No.20 WordPress Plugin "Contest Gallery" vulnerable to cross-site request forgery JVNDB-2019-000036
- CVSSv2 Severity Rating Scale
-
Level I (Low)
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
2.6
- CVSSv3 Severity Rating Scale
-
Medium
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
4.3
- Date Public
-
2019/6/12
- Access Count
-
6,094
Table 3-2 lists the top 5 most accessed vulnerability information among those reported by domestic product developers.
Table 3-2. Top 5 Most Accessed Vulnerabilities Reported by Domestic Product Developers [Oct. - Dec. 2019]
No.1 Vulnerability in Cosminexus HTTP Server and Hitachi Web Server JVNDB-2019-010374
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
- -
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
- -
- Date Public
-
2019/10/11
- Access Count
-
8,116
No.2 Multiple Vulnerabilities in Hitachi Global Link Manager JVNDB-2019-010375
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
- -
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
-
- Date Public
-
2019/10/11
- Access Count
-
6,277
No.3 Multiple Vulnerabilities in Hitachi Command Suite and Hitachi Infrastructure Analytics Advisor JVNDB-2019-008917
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
-
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
-
- Date Public
-
2019/9/9
- Access Count
-
5,867
No.4 Information Disclosure Vulnerability in Hitachi Command Suite
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
-
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
-
- Date Public
-
2019/11/11
- Access Count
-
5,084
No.5 DoS Vulnerability in Hitachi Command Suite and Hitachi Infrastructure Analytics Advisor JVNDB-2019-011487
- CVSSv2 Base Score
-
-
- CVSSv3 Base Score
-
-
- Date Public
-
2019/11/11
- Access Count
-
5,014
Footnotes
-
(*1)
-
(*2)
-
(*3)
-
(*4)
-
(*5)
-
(*6)
-
(*7)
-
(*8)
-
(*9)
-
(*10)
-
(*11)
-
(*12)
-
(*13)
Past Quarterly Reports
Contact information
IT Security Center, Information-technology Promotion Agency, Japan (ISEC/IPA)